19
As shown in
, an inward-facing MEP does not send packets to its host port. Rather, it sends
packets to other ports on the device.
•
MIP
A MIP is internal to an MD. It cannot send CFD packets actively; however, it can handle and respond to
CFD packets. The MA and MD to which a MIP belongs define the VLAN attribute and level of the packets
received.
By cooperating with MEPs, a MIP can perform a function similar to ping and traceroute. Like a MEP, a
MIP forwards packets at a higher level without any processing and only processes packet of its own level
or lower.
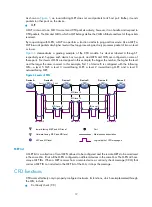
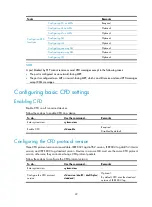
demonstrates a grading example of the CFD module. Six devices labeled A through F
respectively exist. Suppose each device has two ports, and MEPs and MIPs are configured on some of
these ports. Four levels of MDs are designed in this example; the bigger the number, the higher the level
and the larger the area covered. In this example, Port 1 of device B is configured with the following
MPs—a level 5 MIP, a level 3 inward-facing MEP, a level 2 inward-facing MEP, and a level 0
outward-facing MEP.
Figure 6
Levels of MPs
Device A
Device B
Device C
Device D
Device E
Device F
5
5
3
5
5
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
MD level 5
MD level 3
MD Level 2
MD Level 2
MD level 0
Port
5
Outward-facing MEP and MD level
5
MIP and MD level
Maintenance association
Logical path of CFD messages
Port 1
Port 2
MD level 0
MD level 0
3
Inward-facing MEP and MD level
2
2
2
2
MEP list
A MEP list is a collection of local MEPs allowed to be configured and the remote MEPs to be monitored
in the same MA. It lists all the MEPs configured on different devices in the same MA. The MEPs all have
unique MEP IDs. When a MEP receives from a remote device a continuity check message (CCM) that
carries a MEP ID not included in the MEP list of the MA, it drops the message.
CFD functions
CFD works effectively only in properly-configured networks. Its functions, which are implemented through
the MPs, include:
•
Continuity check (CC)