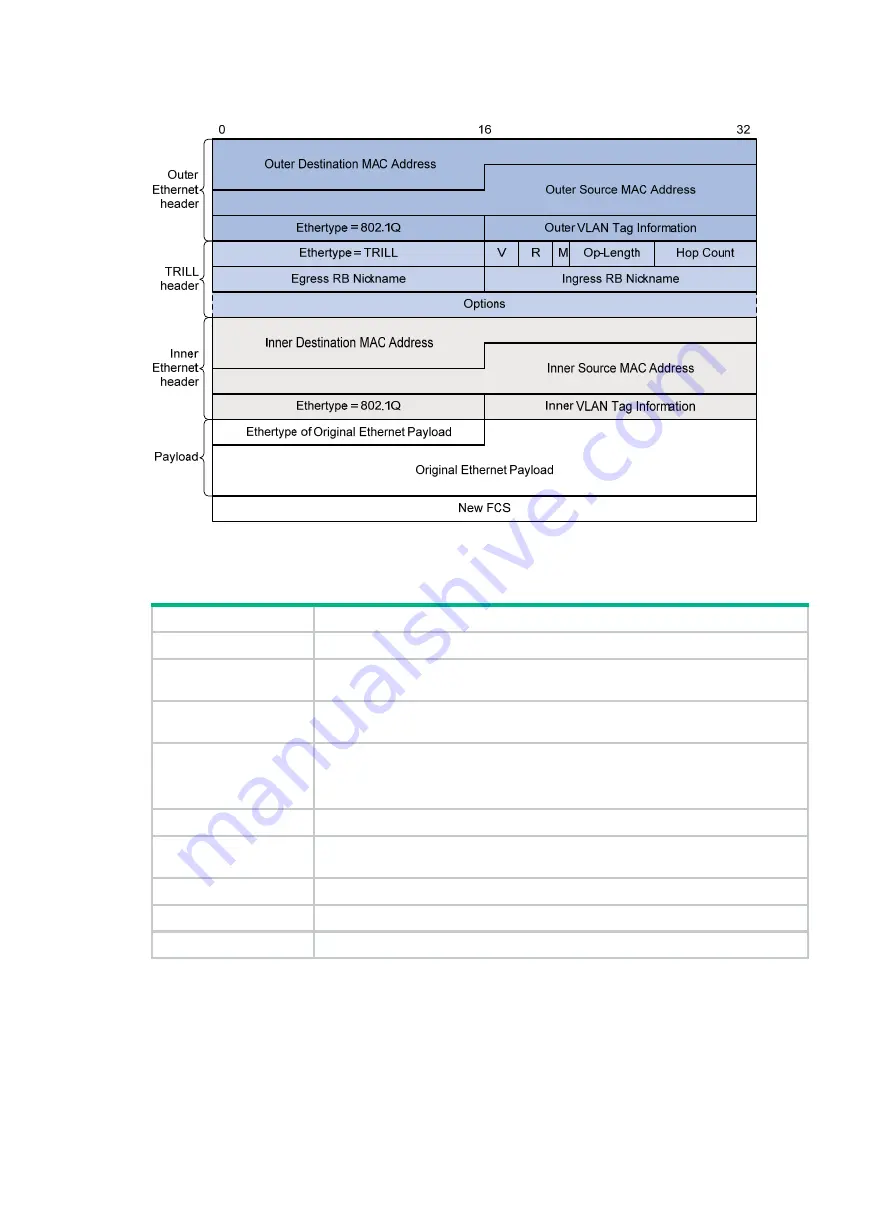
2
Figure 1 TRILL data frame format
describes the fields in the TRILL header.
Table 1 TRILL header fields
Field Description
Ethertype
The Ethertype is fixed to TRILL.
V
Version number, which is 0. When an RB receives a TRILL frame, it checks the
V
field and drops the frame if the
V
field is not 0.
R
Reserved for future extension. An ingress RB sets the R field to
0
when adding a
TRILL header. Transit RBs and egress RBs ignore the field.
M
Multidestination attribute:
•
0
—Known unicast frame.
•
1
—Multidestination frame (multicast, broadcast, or unknown unicast frame).
Op-Length
Length of the
Options
field.
0
indicates that the
Options
field does not exist.
Hop Count
Hop count, which is used to avoid loops. An RB drops a TRILL frame whose hop
count is decremented to 0.
Egress RB Nickname
Nickname of the egress RB.
Ingress RB Nickname
Nickname of the ingress RB.
Options
Options field. This field exists when the
Op-Length
field is non-zero.
How TRILL works
TRILL establishes and maintains adjacencies between RBs by periodically advertising Hello frames,
distributes LSPs among RB neighbors, and generates an LSDB for all RBs in the network. Based on
the LSDB, each RB uses the SPF algorithm to calculate forwarding entries destined to other RBs.























