7
ARP flood suppression
ARP flood suppression reduces ARP request broadcasts on the EVI network by enabling edge
devices to reply to ARP requests on behalf of remote-site hosts.
As shown in
, this feature snoops ARP packets on an EVI tunnel interface to populate the
ARP flood suppression table with remote MAC addresses. If an ARP request has a matching entry,
the local edge device replies to the request on behalf of the remote-site host. If no match is found, the
edge device floods the request to the EVI network.
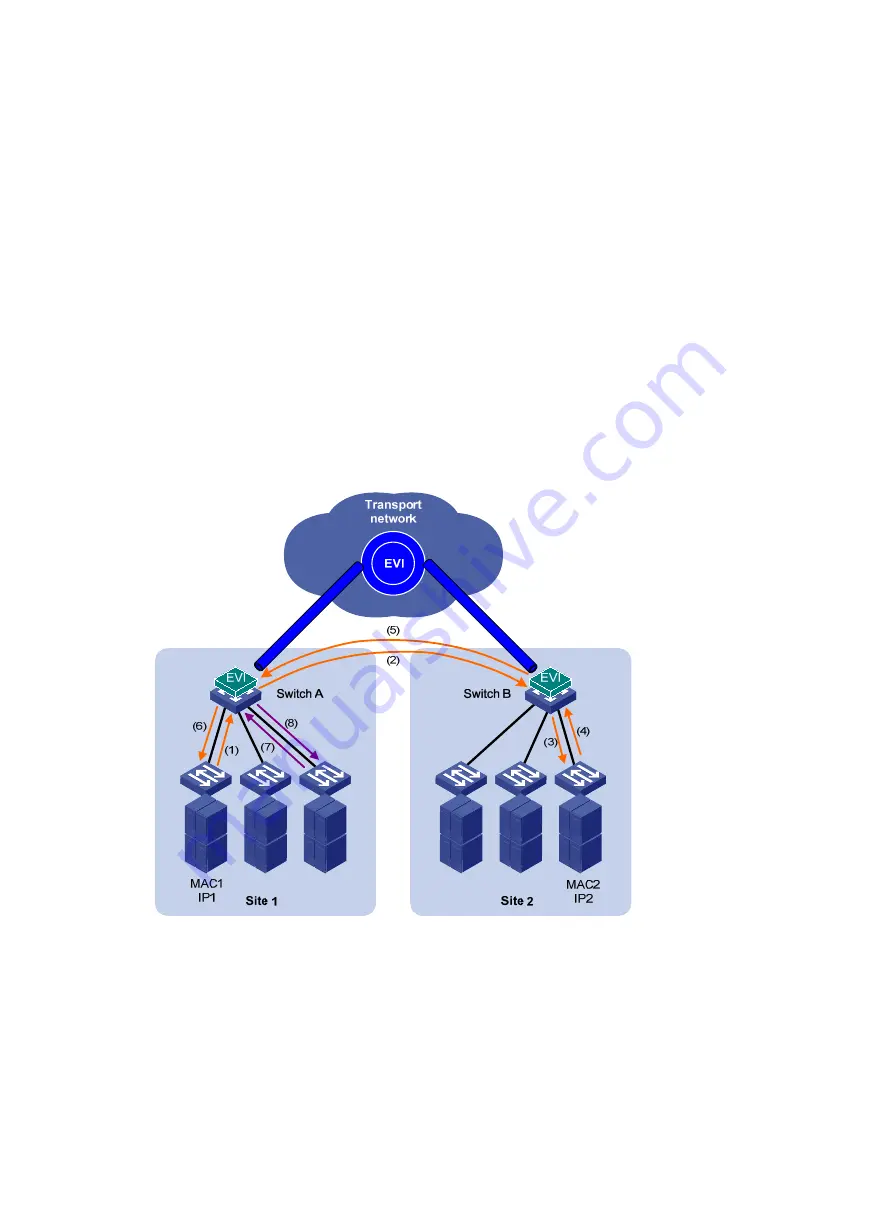
ARP flood suppression uses the following workflow:
1.
Host IP1 in site A sends an ARP request to obtain the MAC address of IP2.
2.
Site A's edge device floods the ARP requests out of all interfaces, including the EVI tunnel
interfaces.
3.
Site B's edge device de-encapsulates the ARP request and broadcasts the request.
4.
IP2 sends an ARP reply back to site A's edge device over the EVI link.
5.
Site A's edge device creates an ARP cache entry for the remote MAC address and forwards the
reply to the requesting host.
6.
Site A's edge device replies to all subsequent requests for the MAC address of IP2.
Figure 6 ARP flood suppression
Selective flooding
Selective flooding enables an edge device to send an unknown unicast or multicast frame out of an
EVI tunnel interface.
This feature is designed for special multicast addresses that require flooding across sites but cannot
be added to a multicast forwarding table by IGMP snooping.