SMA5005 & SMA5015 MANUAL
MANUAL # 5005-2040-000-F UPDATED: 6/1/2021
B. Calibration of the Velocity Mode of a Standard Performance Drive
(SMA5005 Series)
The Drive, in this configuration, receives an analog, bi-polar input command, which is proportional
to the motor velocity. The Drive receives velocity feedback from a tachometer, which is usually
mounted to the rear of the motor. The following pots will be set during calibration: (Note: RV7 is a
single turn pot and RV1-RV5 are 20-turn pots.)
PROCEDURE:
1. Connect motor cables to DC Input/Motor Output pin 4 (MOTOR+) and DC Input/Motor Output
pin 5 (MOTOR-). Connect the motor ground to the chassis ground (or PE).
2. Connect the Tach. wires to Controller I/O pin 3 (TACH IN-) and Controller I/O pin 4 (TACH IN+
‘GND’).
3. Apply main power and fan power. Visually confirm a green LED. Depending on the
configuration of the Inhibit, Reset and +/-Limits, it may be necessary to make appropriate
connections to those terminals before the Drive will be enabled and energize the motor.
4. Slowly turn the Loop Gain (RV7) CW fully. Motor should be stopped or turning slowly. If the
motor starts running away, remove the power, reverse the Tach. leads, and apply power.
5. Set Balance (RV2) for zero motor rotation.
6. Connect oscilloscope probe to Controller I/O pin 7 (CURRENT SENSE) and oscilloscope
ground to Controller I/O pin 13, 14 or 15 (SIGNAL GND). Connect battery box to Controller I/O
pin 1 () and Controller I/O pin 2 (SIGNAL-). The voltage on Controller I/O pin 7 is a
function of motor current: 1V = 2.0A. While applying a step input voltage, adjust the Current
Limit (RV5) for desired peak current.
7. The purpose of the following procedure is to set the system bandwidth to obtain a critically-
damped response (see figure B) or a one hook overshoot response with the maximum possible
Tach. Gain. There are many possible settings of Tach. Gain and Compensation which will yield
the desired waveform: The optimum setting will occur when Tach. Gain is as CW as possible
and Compensation is as CCW as needed. However, the velocity loop may become unstable
(the motor oscillates or hums) as the Compensation is tuned CCW (increasing the BW). In this
case, stability is the limiting factor: At no time should the velocity loop be allowed to be
unstable. Drives are normally shipped with the Tach. Gain (RV4) set at 100%. This is a good
place to start. If you are unsure of where the Tach. Gain is set, turn the Tach. Gain (RV4) fully
CW (up to 20 turns).
8. Connect oscilloscope probe to Controller I/O pin 3 (TACH IN-) and oscilloscope ground to
Controller I/O pin 13, 14 or 15. Set battery box for a DC signal output to obtain approximately
400RPM. The RPM may be set by measuring the Tach. voltage at Controller I/O pin 3, e.g.,
2.8VDC for a 7V/KRPM Tach. is 400RPM.
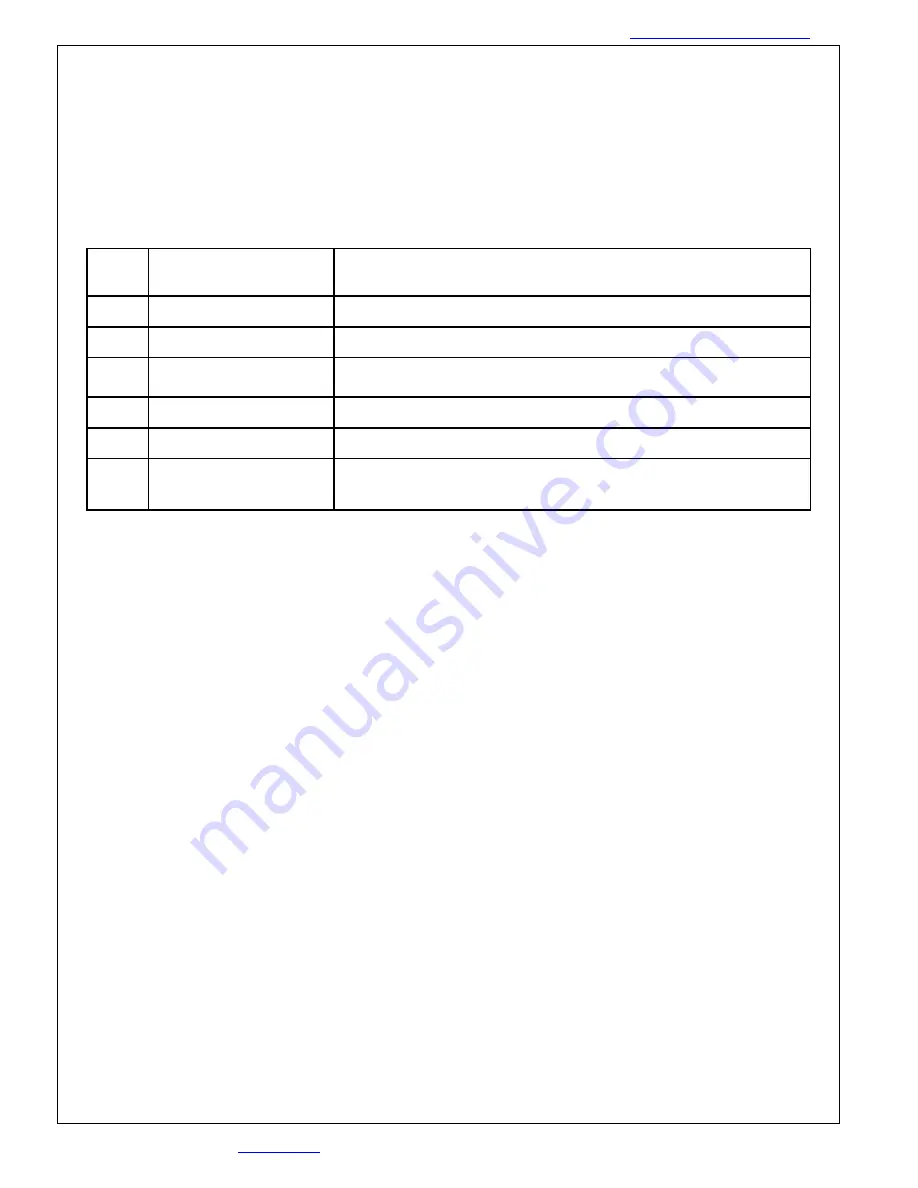
Pots
Name of Pot
Notes
RV1
Signal Gain,
SIG
Sets the input voltage to velocity ratio.
RV2
Balance,
BAL
Used to null any offset in the system.
RV3
Compensation,
COMP
Used in conjunction with Tach. Gain to set the system
bandwidth.
RV4
Tach. Gain,
TACH
Sets the DC tachometer gain.
RV5
Current Limit,
I LIMIT
Sets the maximum motor current. Shipped set CW (max).
RV7
Loop Gain,
LOOP GAIN
Used to shut off uncalibrated Drives. When the loop gain is fully
CCW, no current is delivered to the motor.



























