&
Start signal
Trip Signal
&
Timer Blocking signals
1
V00654
Timer Settings
Threshold
IDMT/DT
Timer Blocking settings
Stage Blocking signals
1
Stage Blocking settings
Function inhibit
Directional Check
&
Energising quantity
Voltage
Current
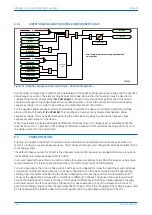
Figure 25: Principle of protection function implementation
An energising quantity is either a voltage input from a system voltage transformer, a current input from a system
current transformer or another quantity derived from one or both of these. The energising quantities are extracted
from the power system. The signals are converted to digital quantities where they can be processed by the IEDs
internal processor.
In general, an energising quantity, be it a current, voltage, power, frequency, or phase quantity, is compared with a
threshold value, which may be settable, or hard-coded depending on the function. If the quantity exceeds (for
overvalues) or falls short of (for undervalues) the threshold, a signal is produced, which when gated with the
various inhibit and blocking functions becomes the Start signal for that protection function. This Start signal is
generally made available to Fixed Scheme Logic (FSL) and Programmable Scheme Logic (PSL) for further
processing. It is also passed through a timer function to produce the Trip signal. The timer function may be an
IDMT curve, or a Definite Time delay, depending on the function. This timer may also be blocked with timer
blocking signals and settings. The timer can be configured by a range of settings to define such parameters as the
type of curve, The Time Multiplier Setting, the IDMT constants, the Definite Time delay etc.
In General Electric products, there are usually several independent stages for each of the functions, and for three-
phase functions, there are usually independent stages for each of the three phases.
Typically some stages use an Inverse Definite Minumum time (IDMT) timer function, and others use a Definite Time
timer (DT) function. If the DT time delay is set to '0', then the function is known to be "instantaneous". In many
instances, the term 'instantaneous protection" is used loosely to describe Definite Time protection stages, even
when the stage may not theoretically be instantaneous.
Many protection functions require a direction-dependent decision. Such functions can only be implemented where
both current and voltage inputs are available. For such functions, a directional check is required, whose output can
block the Start signal should the direction of the fault be wrong.
Note:
In the logic diagrams and descriptive text, it is usually sufficient to show only the first stage, as the design principles for
subsequent stages are usually the same (or at least very similar). Where there are differences between the functionality of
different stages, this is clearly indicated.
3.2.1
TIMER HOLD FACILITY
The Timer Hold facility is available for stages with IDMT functionality , and is controlled by the timer reset settings
for the relevant stages (e.g. I>1 tReset, I>2 tReset ). These cells are not visible for the IEEE/US curves if an inverse
time reset characteristic has been selected, because in this case the reset time is determined by the time dial
setting (TDS).
Chapter 6 - Current Protection Functions
P24xM
92
P24xM-TM-EN-2.1
Summary of Contents for P24DM
Page 2: ......
Page 17: ...Appendix C Wiring Diagrams 467 P24xM Contents P24xM TM EN 2 1 xv...
Page 18: ...Contents P24xM xvi P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 24: ...Table of Figures P24xM xxii P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 25: ...CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION...
Page 26: ...Chapter 1 Introduction P24xM 2 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 37: ...CHAPTER 2 SAFETY INFORMATION...
Page 38: ...Chapter 2 Safety Information P24xM 14 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 51: ...CHAPTER 3 HARDWARE DESIGN...
Page 52: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design P24xM 28 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 66: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design P24xM 42 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 67: ...CHAPTER 4 SOFTWARE DESIGN...
Page 68: ...Chapter 4 Software Design P24xM 44 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 77: ...CHAPTER 5 CONFIGURATION...
Page 78: ...Chapter 5 Configuration P24xM 54 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 94: ...Chapter 5 Configuration P24xM 70 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 95: ...CHAPTER 6 CURRENT PROTECTION FUNCTIONS...
Page 96: ...Chapter 6 Current Protection Functions P24xM 72 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 188: ...Chapter 6 Current Protection Functions P24xM 164 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 189: ...CHAPTER 7 RESTRICTED EARTH FAULT PROTECTION...
Page 190: ...Chapter 7 Restricted Earth Fault Protection P24xM 166 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 201: ...CHAPTER 8 CB FAIL PROTECTION...
Page 202: ...Chapter 8 CB Fail Protection P24xM 178 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 215: ...CHAPTER 9 CURRENT TRANSFORMER REQUIREMENTS...
Page 216: ...Chapter 9 Current Transformer Requirements P24xM 192 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 224: ...Chapter 9 Current Transformer Requirements P24xM 200 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 225: ...CHAPTER 10 VOLTAGE PROTECTION FUNCTIONS...
Page 226: ...Chapter 10 Voltage Protection Functions P24xM 202 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 245: ...CHAPTER 11 FREQUENCY PROTECTION FUNCTIONS...
Page 246: ...Chapter 11 Frequency Protection Functions P24xM 222 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 261: ...CHAPTER 12 POWER PROTECTION FUNCTIONS...
Page 262: ...Chapter 12 Power Protection Functions P24xM 238 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 265: ...CHAPTER 13 MONITORING AND CONTROL...
Page 266: ...Chapter 13 Monitoring and Control P24xM 242 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 294: ...Chapter 13 Monitoring and Control P24xM 270 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 295: ...CHAPTER 14 SUPERVISION...
Page 296: ...Chapter 14 Supervision P24xM 272 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 312: ...Chapter 14 Supervision P24xM 288 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 313: ...CHAPTER 15 DIGITAL I O AND PSL CONFIGURATION...
Page 314: ...Chapter 15 Digital I O and PSL Configuration P24xM 290 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 327: ...CHAPTER 16 COMMUNICATIONS...
Page 328: ...Chapter 16 Communications P24xM 304 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 386: ...Chapter 16 Communications P24xM 362 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 387: ...CHAPTER 17 CYBER SECURITY...
Page 388: ...Chapter 17 Cyber Security P24xM 364 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 405: ...CHAPTER 18 INSTALLATION...
Page 406: ...Chapter 18 Installation P24xM 382 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 419: ...CHAPTER 19 COMMISSIONING INSTRUCTIONS...
Page 420: ...Chapter 19 Commissioning Instructions P24xM 396 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 443: ...CHAPTER 20 MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING...
Page 444: ...Chapter 20 Maintenance and Troubleshooting P24xM 420 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 453: ...CHAPTER 21 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS...
Page 454: ...Chapter 21 Technical Specifications P24xM 430 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 486: ...Chapter 21 Technical Specifications P24xM 462 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 487: ...APPENDIX A ORDERING OPTIONS...
Page 488: ...Appendix A Ordering Options P24xM 464 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 491: ...APPENDIX B SETTINGS AND SIGNALS...
Page 493: ...APPENDIX C WIRING DIAGRAMS...
Page 494: ...Appendix C Wiring Diagrams P24xM 468 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 497: ......
Page 498: ......
Page 499: ......
Page 500: ......
Page 501: ......
Page 502: ......
Page 503: ......
Page 504: ......
Page 505: ......
Page 506: ......
Page 507: ......
Page 508: ......
Page 509: ......
Page 510: ......
Page 511: ......
Page 512: ......
Page 513: ......
Page 514: ......
Page 515: ......
Page 516: ......
Page 517: ......
Page 518: ......
Page 519: ......
Page 520: ......
Page 521: ......
Page 522: ......
Page 523: ......
Page 524: ......
Page 525: ......
Page 526: ......
Page 527: ......
Page 528: ......
Page 529: ......
Page 530: ......
Page 531: ......
Page 532: ......
Page 533: ......
Page 534: ......
Page 535: ......
Page 536: ......
Page 537: ......
Page 538: ......
Page 539: ......
Page 540: ......
Page 541: ......
Page 542: ......
Page 543: ......
Page 544: ......
Page 545: ......
Page 546: ......
Page 547: ......
Page 548: ......
Page 549: ......
Page 550: ......
Page 551: ......
Page 552: ......
Page 553: ......
Page 554: ......
Page 555: ......
Page 556: ......
Page 557: ......
Page 558: ......
Page 559: ......
Page 560: ......
Page 561: ......
Page 562: ......
Page 563: ......
Page 564: ......
Page 565: ......
Page 566: ......
Page 567: ......
Page 568: ......
Page 569: ......
Page 570: ......
Page 571: ......
Page 572: ......
Page 573: ......
Page 574: ......
Page 575: ......
Page 576: ......
Page 577: ......
Page 578: ......
Page 579: ......
Page 580: ......
Page 581: ......
Page 582: ......
Page 583: ......
Page 584: ......
Page 585: ......
Page 586: ......
Page 587: ......
Page 588: ......
Page 589: ......
Page 590: ......
Page 591: ......
Page 592: ......
Page 593: ......
Page 594: ......
Page 595: ......
Page 596: ......
Page 597: ......
Page 598: ......
Page 599: ......