CB Watch 3 User Manual
v6.3 - May 2019
Page 36 of 100
SF6 GAS MONITORING
General Description
If the circuit breaker being monitored uses SF6 gas (or gas mixture) to extinguish the arc,
then the CBW3 can monitor the gas tanks for leaks.
During commissioning, a circuit breaker is filled with gas to its nominal filling density. The
performance and even operation of a circuit breaker can be severely affected if the
density of the gas contained in the circuit breaker falls too low.
During the CB’s
life, it is
therefore necessary to monitor the density of the gas not only to alert maintenance that
a re-fill operation is needed before the CB locks itself (preventing operation) but also to
detect any gas leak early so as to reduce cost, avoid penalties and save the environment.
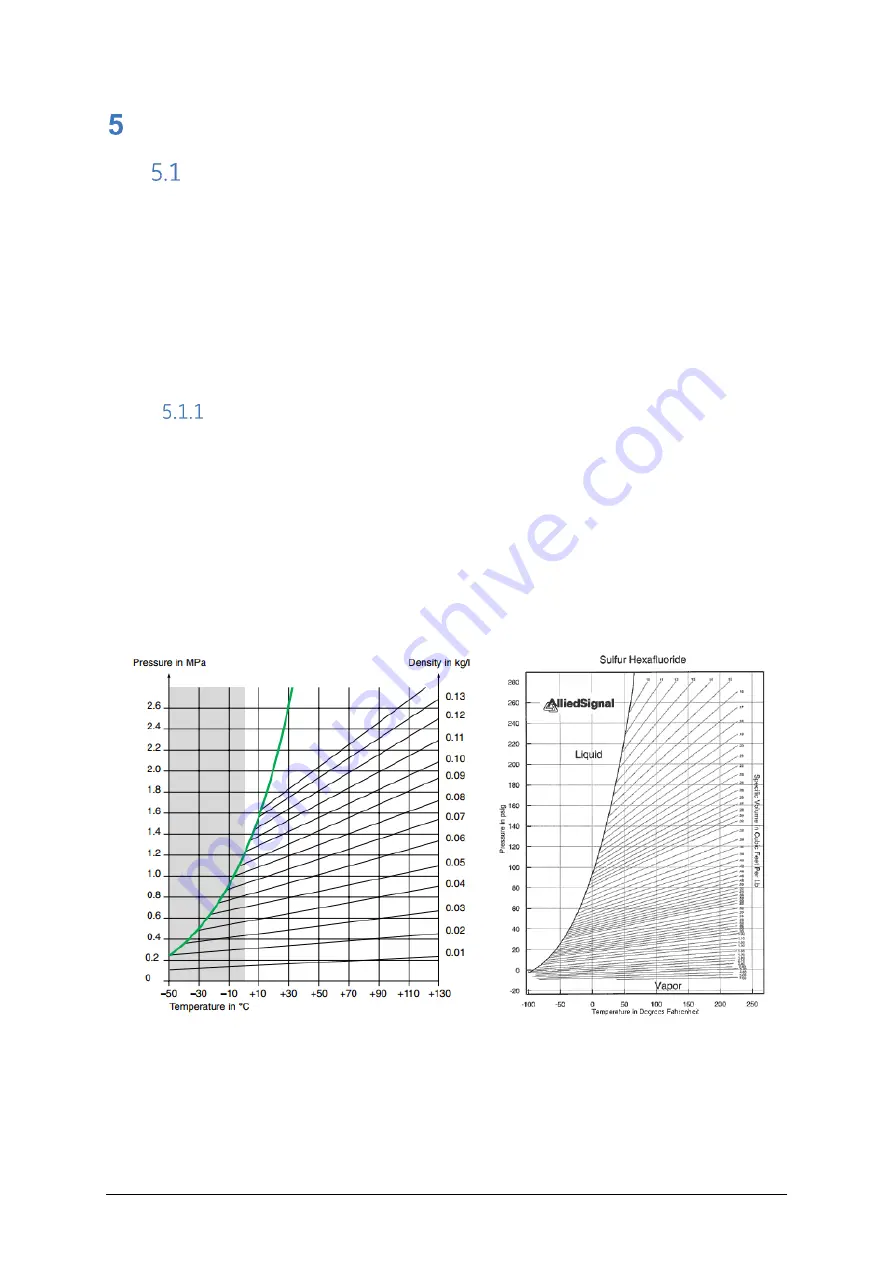
Measurement principle
Because gas pressure varies with temperature (see figure below), pressure values cannot
be compared over time unless they are temperature compensated. The variation of
pressure with temperature is linear in the range of service (-25
o
C to +50
o
C). Comparisons
are therefore made using either
“
pressure normalised at 20
o
C
”
or
“
density
”
(expressed in
kg/m3 or gr/l) which is independent.
The gas pressure and gas temperature are measured by the sensor and then the gas
density is calculated using the Beattie-Bridgeman equation to take into account the
thermodynamic laws of the gas (or gas mixture) used,.
Figure 46
–
Thermodynamic law applied to SF6 gas
These diagrams show lines of equivalent density where, along each line, the gas has the
same density for various temperature/pressure combinations.















































