XG Series User's Guide
Chapter 4 Switch Functions and their Configuration
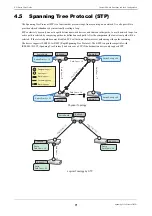
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
72
4.5.1
Port Roles Based on Spanning Tree
RSTP assigns one of these port roles to individual ports:
•
Root port
Provides the best path (lowest cost) when the switch forwards packets to the root switch.
•
Designated port
Connects to the designated switch toward the leaves of the spanning tree. The port specified connecting to the
designated port serves as a root port.
•
Alternate Port
The alternative port with the second lowest path cost. In the event that the root port goes to a linkdown state, the
alternate port serves as the root port. It does not always send or receive frames while in the blocking state.
•
Backup Port
Provides an alternative path to that specified. In the event that the specified port goes into a linkdown state, the backup
port serves as the new designated port. It does not always send or receive frames while it is in the blocking state.
•
Disabled Port
Disabled port, it does not send or receive any frames.
4.5.2
Spanning Tree Protocol Port States
The port states defined by the STP are:
•
Discard
The port is in a "discarding state. BPDUs are only received.
•
Learn
The port is in a "learning" state. A port in the learning state learns the destination MAC address of the received frames
but does not participate in frame forwarding.
•
Forward
The port is ready to transmit data traffic.
The STP states "blocking" and "listening" have been merged into a unique RSTP "discarding" state. The correspondence
between STP port states and RSTP port states are shown below.
Display Format
STP (IEEE802.1D)
RSTP (IEEE802.1w)
Discard
Blocking
Discarding
Discard
Listening
Discarding
Learn
Learning
Learning
Forward
Forwarding
Forwarding