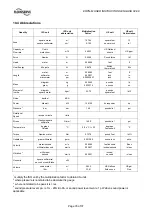
ERPN-M USER INSTRUCTIONS ENGLISH 02-08
Page 22 of 37
5.3 Impeller clearance
No axial adjustment of the rotor is necessary.
5.4 Direction of rotation
The sense of rotation of the
pump is clockwise (CW); looking from the coupling to
the shaft end of the pump.
The rotation of the driver shall be checked.
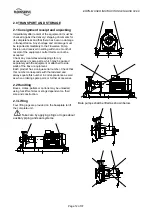
5.5 Guarding
Be sure that the coupling guard is mounted correctly
at the baseplate prior to start up.
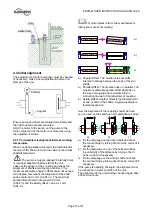
5.6 Priming and auxiliary supplies
The pump must be completely primed prior to start
up.
a) The pump casing is considered as self venting,
so no vent connections are provided.
b) Auxiliary systems, e.g. barrier /buffer fluid
systems, cooling circuits, shall be filled according
to the user instructions.
5.7 Starting the pump
a) Start the driver according to the specification.
(Refer to driver IOM).
Pumps are usually started against
closed discharge valve.
b)
Check the discharge and suction pressure gauge
to verify the pumps delivered head. Open the
discharge valve slowly, until the pump reaches the
specified operation point. The pump must operate
smoothly, and the vibration must be below 3 mm/s
(0.2 in./sec) (API 610 vibration limits).
The discharge valve must be opened
within 10 sec. after start up. Longer operation
against closed discharge valve will damage the
pump. If a minimum flow valve is installed, take
pressure gauge readings to verify the correct
operation.
If the backpressure of the discharge
pipe is sufficient, pumps can be started against
open valve.
Ensure that your driver is capable deliver
the higher torque required by starting against
open valve.
To prevent the pump from reverse rotation
after shut down, the installation of a check valve
is recommended.
Check the discharge and suction pressure gauge
to verify the pumps delivered head.
The pump must operate smoothly, and the
vibration must be below 3 mm/s (0.2 in./sec) (API
610 vibration limits).
If a minimum flow valve is installed, take pressure
gauge readings to verify the correct operation.
c) Check the pipe system against any leakage.
d) Check the magnetic coupling against any leakage.
Check temperature of the can to
avoid damage of the Silicon Carbide bearings.
5.8 Operation
a) Verify that the pump is operating within the
specified limits, min/max flow, pressure,
temperature, vibration, power
b) The bearing housing temperature shall not exceed
80 °C (176 °F). If higher bearing temperature are
observed, check the viscosity grade of the used
lubrication oil.
The minimum viscosity is 10
cSt at the expected oil temperature.
(Oil temperature = bearing gland temperature
+ 10 °C (+50 °F))
c) Check if the temperature monitoring system is
working correctly. It is essential that any abnormal
temperature increase is detected immediately.
(The max. temperature shall not exceed the fluid
tempe20 °C (+68 °F)). Therefore we strictly
recommend to include the temperature monitoring
system into your process control.
d) Observe the power consumption of the pump to
detect excessive wear.
5.9 Stopping and Shutdown
a) Close the outlet valve, but ensure that the pump
runs in this condition for no more than a few
seconds.
b) Stop the pump.
c) Switch off flushing and/or cooling/ heating liquid
supplies at a time appropriate to the process.
d) For prolonged shut-downs and especially when
ambient temperatures are likely to drop below
freezing point, the pump and any cooling and
flushing arrangements must be drained or
otherwise protected.
For automatic start/stop operation of the
pump, ensure that all steps described in chapter 5.6,
5.7, 5.8 and 5.9 are implemented in the control logic.