ESBF-BS/-LS
Electric cylinder
Festo SE & Co. KG
Ruiter Straße 82
73734 Esslingen
Deutschland
+49 711 347-0
www.festo.com
Operating instructions
8155148
2021-04d
[8155150]
Translation of the original instructions
© 2021 all rights reserved to Festo SE & Co. KG
1
Applicable Documents
All available documents for the product
2
Safety
2.1
Safety instructions
–
Observe labelling on the product.
–
Prior to assembly, installation and maintenance work: Switch off power supply,
ensure that it is off and secure it against being switched back on.
–
Store the product in a cool, dry, UV-protected and corrosion-protected environ-
ment. Ensure that storage times are kept to a minimum.
–
Observe tightening torques. Unless otherwise specified, the tolerance
is ± 20 %.
2.2
Intended Use
The electric cylinder is intended to be used for positioning payloads in combina-
tion with tools or as a drive when external guides are used.
2.3
Training of qualified personnel
Work on the product may only be carried out by qualified personnel who can
evaluate the work and detect dangers. The qualified personnel have knowledge
and experience in handling electric drives and axes.
3
Additional information
–
Contact the regional Festo contact if you have technical problems
–
Accessories and spare parts
4
Product overview
4.1
Function
The electric cylinder converts the rotary motion of the mounted motor into a linear
motion of the non-rotating piston rod. The lead screw converts the torque of the
motor into a feed force. The linear movement of the piston rod is precisely guided
by the guide in the bearing cap. Sensors enable the monitoring of end positions,
reference position and intermediate position.
Lead screw ESBF-LS
Ball screw drive ESBF-BS
–
Low speeds
–
Self-braking with de-energised motor (without
brake)
–
High speeds
–
High forces
Tab. 1: Overview of Lead Screw
4.2
Product design
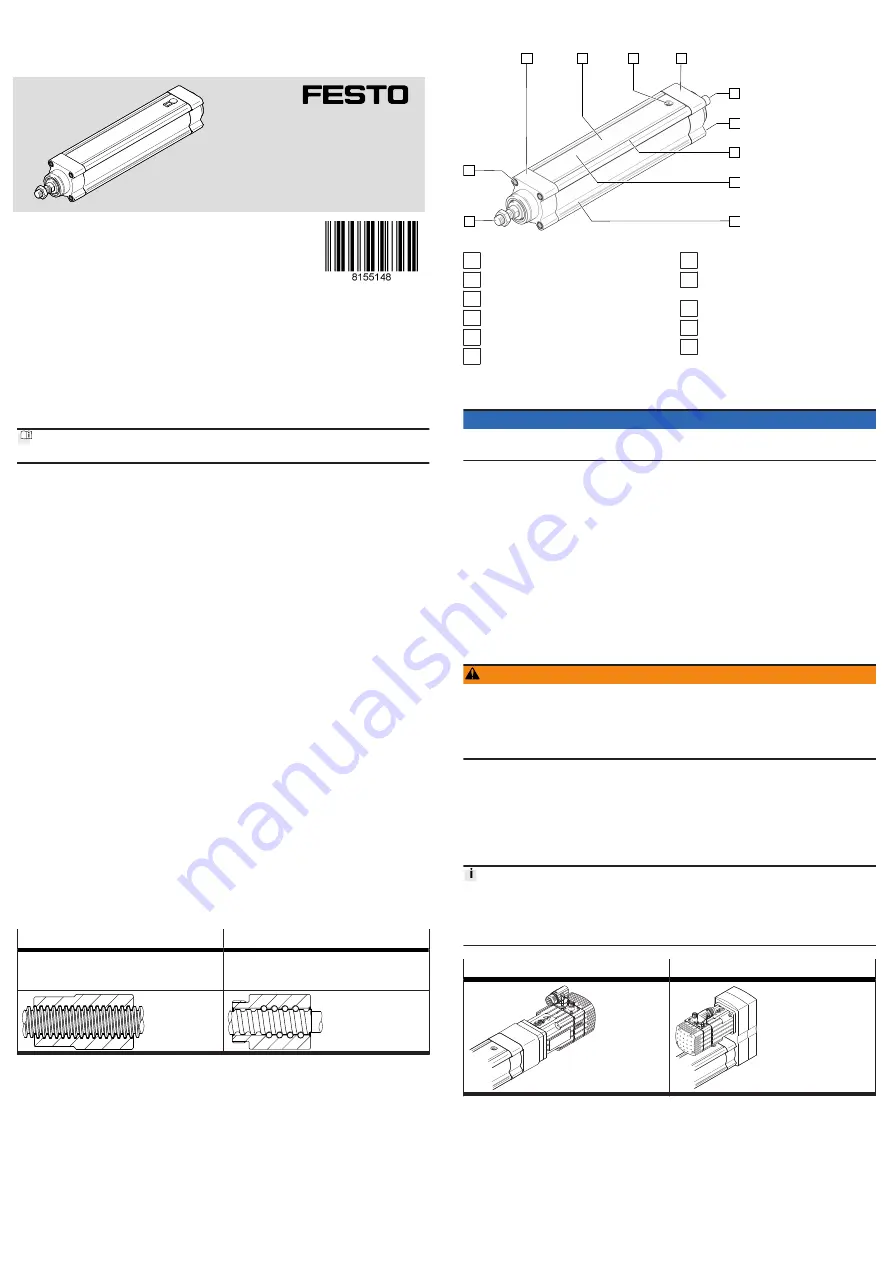
ESBF product design
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Fig. 1: ESBF product design (example ESBF-BS)
1 Piston rod
2 Threaded hole for mounting
3 Bearing cap
4 Cylinder profile
5 Pressure compensation port
6 Drive cover
7 Drive shaft
8 Threaded hole for motor
mounting kit
9 Interface for sensor bracket
10 Interface for sensor rail
11 Interface for profile mounting
5
Transport and Storage
NOTICE
Unexpected and unbraked movement of components
• Secure moving components for transport.
Transport and Storage Conditions
–
Take product weight into account
Weight > 25 kg: transport with a suitable hoist (cross-brace) or with two per-
sons.
–
Take the product focus into consideration.
–
Store and transport the product in its original packaging.
–
Store product in a cool, dry, shaded and corrosion protected environment.
–
Store product in ambient conditions without oils, greases and degreasing
vapours.
–
Ensure short storage times.
6
Assembly
6.1
Safety
WARNING
Risk of Injury due to Unexpected Movement of Components
For vertical or slanted mounting position: when power is off, moving parts can
travel or fall uncontrolled into the lower end position.
• Bring moving parts of the product into a safe end position or secure them
against falling.
6.2
Unpacking
1. Open packaging.
2. Remove all transport materials (e.g. foils, caps, cardboard boxes).
3. Remove the product from the packaging and place it on the mounting surface.
4. Dispose of packaging and transport materials.
6.3
Mounting the motor
Transverse load on the drive shaft
When mounting the motor and motor mounting kit, do not exceed the maximum
transverse load F
R
of the drive shaft (for example toothed belt tension when
mounting the parallel kit)
Axial kit EAMM-A
Parallel kit EAMM-U
Tab. 2: Overview of motor mountings
Requirement
–
Only loosen screws or threaded pins that are described in the directions in the
instruction manuals.
–
Sufficient space for reaching and mounting the pressure compensation port
Connecting pressure compensation (ESBF -...- S1 only).
1. Select the motor and motor mounting kit from
Festo
If other motors are used: observe the critical limits for forces, torques and
velocities.


























