PCoIP Technology User Guide
22
9 Latency
Considerations
Every network has latency effects that may
require attention. Latency effects keyboard,
mouse and display response. These effects are
user subjective with some users noticing effects
more than others.
Some latency considerations:
•
Latency due to length of physical medium (i.e.
speed of light of copper/fiber) and switch hops
•
Additional latency due to OS overhead (e.g.
40-50 ms for Windows)
The table below describes latency effects based
on critical user evaluation.
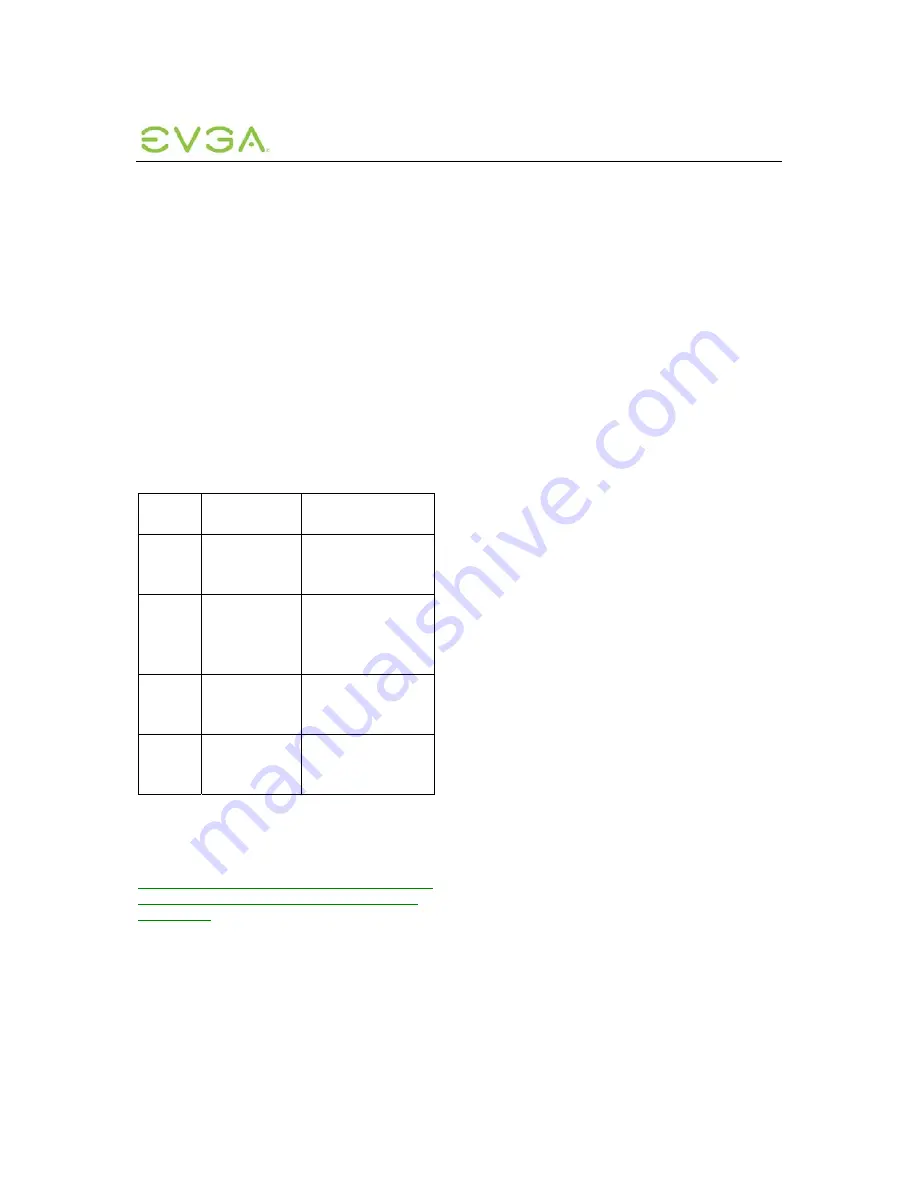
Table 9-1: Latency Observations
Network
Latency
Approximate
Distance
1
User Observations
0-30
ms
Campus/metro/
inter-city
(0-1500km)
Perception free to
average user
40-60
ms
Inter-city/intra-
country
(1500-2500km)
Minimal latency
perceived, e.g.
‘heavy’ mouse and
window movement,
but very usable
60-100
ms
Intra-country/
inter-continent
(2500-5000km)
Sluggish mouse and
windows; some audio
dropouts
> 100
ms
Inter-continent/
overseas
(> 5000km)
Slow mouse and
windows; audio
dropouts
1
High bandwidth, low-error network
Note: As with bandwidth considerations, these
latency observations are subjective and biased
towards a perception free experience.
Administrators must study use case(s) typical for
their deployment and adjust user expectations
accordingly.
USB Latency Performance
Latency effects observed for USB performance
depend on the type of data transfer.
•
Isochronous - may notice delay or loss of data
(e.g. video data lost when using a webcam)
•
Interrupt - may delay device response (e.g.
slow keyboard keystrokes)
•
Bulk - may notice slower data transfer (e.g.
slower USB flash drives)
Desired Network Attributes
Latency effects can be minimized by using a
network with these attributes:
•
High bandwidth
•
Low error rate
•
Minimized data path/network hops
Minimizing Latency Effects
Often latency effects can not be avoided due to
extreme long distances, non-optimal networks,
etc. Administrators can minimize bandwidth use
and therefore reduce latency effects by:
•
Using less graphically-demanding applications
(and setting user expectations accordingly)
•
Using
Device Bandwidth Target
and
Device
Bandwidth Limit
settings to limit bandwidth
usage to minimum requirements (see Section
6, Bandwidth Considerations)
•
Configuring image settings to minimum image
quality requirements (see Section 7, Imaging
Considerations)




































