EPSON Stylus COLOR 900/900N
Chapter 2 Operating Principles
36
2.2.2.2 Printhead Drive Control
The printhead includes one piezoelectric element (PZT) for each
nozzle, or 480 in all. When the printer applies voltage to a PZT, the PZT
compresses the ink cavity located directly beneath it and ink ejects from
the nozzle as a result.
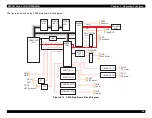
Figure 2-2. Printer Mechanism Block Diagram
As shown in the illustration above, the ASIC processes temperature and
other data to regulate the main drive pulse (trapezoidal waveform) that
drives the printhead. This signal is generated by four power transistors
located on the main board.
Before each pulse is generated, the ASIC transfers five strings of serial
data (one for each row of nozzles) to the nozzle selector IC in the
printhead. The nozzle selector holds open, or latches, a selection of
transistorized gates that corresponds to the pattern of nozzles to be
fired. When the main drive pulse arrives at the printhead, it passes
though only those gates that have been latched open, and the desired
pattern of PZTs fires as a result.
2.2.2.3 Temperature Regulation
The printhead produces a large quantity of heat because it contains
many drive elements (480) and they operate at a fast drive frequency
(32.4 KHz).
If the printhead is driven with blocked nozzles, heat generated by the
PZTs cannot be released. To prevent damage, the printhead contains
five thermistors to monitor the temperature of each nozzle row. If the
temperature rises above 100
°
C (which occurs when about half the
nozzles in any row are blocked), the printer automatically enters the
CL2 cleaning mode, the most powerful cleaning cycle. This unclogs
blocked nozzles and restores ink flow to cool the printhead.
If the cleaning cycle fails to reduce the temperature below 100
°
C, the
printer assumes that many nozzles remain clogged. It then displays an
Ink Out error, which forces the user to replace the ink cartridges.
Replacing the ink cartridges may help remedy the clogged nozzles
because:
The ink cartridges may be more than six months old and beyond
their useful life (because of thickened ink).
The user may have repeatedly removed and reinstalled an ink
cartridge. This causes the Ink Consumption Counter to lose
track of the actual ink supply. Eventually, the printer may try to
print even after the ink has completely run out.
If the user removed an ink cartridge, air bubbles may have
entered it and blocked the nozzles.
A strong jolt may have dislodged ink from the nozzles’ surface.
Besides using temperature data to prevent excessive heat buildup, the
printer also uses it to subtly change the voltage level of the drive pulse
to maintain consistent printing. For more information, see
N o z z l e
S e l e c t o r
P r e -
D r i v e r
+ 4 2
D r i v e r
D a t a
L a t c h
C h a r g e
D i s - c h a r g e
P Z T
C a v i t y
N o z z l e P l a t e
A S I C
N o z z l e
P u l s e
P u l s e f o r m c o m m a n d
T e m p e r a t u r e d a t a
T e m p e r a t u r e
d e t e c t i o n
c i r c u i t
L a t c h
c i r c u i t
Summary of Contents for 900N
Page 1: ...EPSONStylusCOLOR900 900N Color ink jet printer TM SC900 N 6 59 0 18 ...
Page 8: ... 37 5 PRODUCTDESCRIPTION ...
Page 37: ... 37 5 OPERATINGPRINCIPLES ...
Page 67: ... 37 5 TROUBLESHOOTING ...
Page 89: ... 37 5 DISASSEMBLYANDASSEMBLY ...
Page 121: ... 37 5 ADJUSTMENTS ...
Page 156: ... 37 5 MAINTENANCE ...
Page 169: ... 37 5 APPENDIX ...
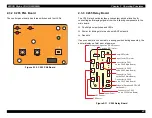
Page 179: ...EPSON Stylus COLOR 900 900N Chapter 7 Appendix 176 Figure 7 3 C265 Main Board Soldering side ...
Page 181: ...EPSON Stylus COLOR 900 900N Chapter 7 Appendix 178 Figure 7 6 C265 PNL Board ...
Page 195: ...06 03 01 02 for S E ASIA 03 03 05 03 04 EPSON STYLUS COLOR 900 No 7 10056 Rev 01 ...
Page 197: ......
Page 198: ......
Page 199: ......
Page 200: ......
Page 201: ......