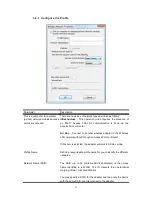
Parameter
Description
Network Key
The keys are used to encrypt data transmitted in the wireless
network. Fill the text box by following the rules below.
64-bit
– Input 10-digit Hex values as the encryption keys. For
example: “0123456aef“.
128-bit
– Input 26-digit Hex values as the encryption keys. For
example: “01234567890123456789abcdef“.
Confirm Network Key
Enter the same network key to confirm.
EAP Type
GTC
– GTC is an authentication protocol which allows the
exchange of clear text authentication credentials across the
network.
TLS
– TLS is the most secure of the EAP protocols but not easy
to use. It requires that digital certificates be exchanged in the
authentication phase. The server presents a certificate to the
client. After validating the server’s certificate, the client presents a
client certificate to the server for validation.
LEAP
– LEAP is a pre-EAP, Cisco-proprietary protocol, with many
of the features of EAP protocols. Cisco controls the ability of other
vendors to implement this protocol, so it should be selected for
use only when limited vendor choice for client, access-point, and
server products is not a concern. When you have set up LEAP
authentication, you have to enter the user name and password of
your computer.
PEAP & TTLS
– PEAP and TTLS are similar and easier than TLS
in that they specify a stand-alone authentication protocol be used
within an encrypted tunnel. TTLS supports any protocol within its
tunnel, including CHAP, MSCHAP, MSCHAPv2 and PAP. PEAP
specifies that an EAP-compliant authentication protocol must be
used; this adaptor supports MD5, TLS, GTC (Generic Token
Card) and MSCHAPv2. The client certificate is optional required
for the authentication.
Tunnel
Includes MD5, GTC, TLS, CHAP, MSCHAP, MSCHAP-v2 and
PAP.
Username
The certificate username in the RADIUS server.
Identity
User’s identity in the RADIUS server.
Password
User’s password in the RADIUS server.
Certificate
The certificate for RADIUS server for certification.
24