ESR-Series. User manual
358
1.
2.
3.
4.
Solution:
ESR
ESR(config)# system cpu load-balance mpls passenger ip
ESR(config)# system cpu load-balance mpls passenger ipoe-pw-without-cw
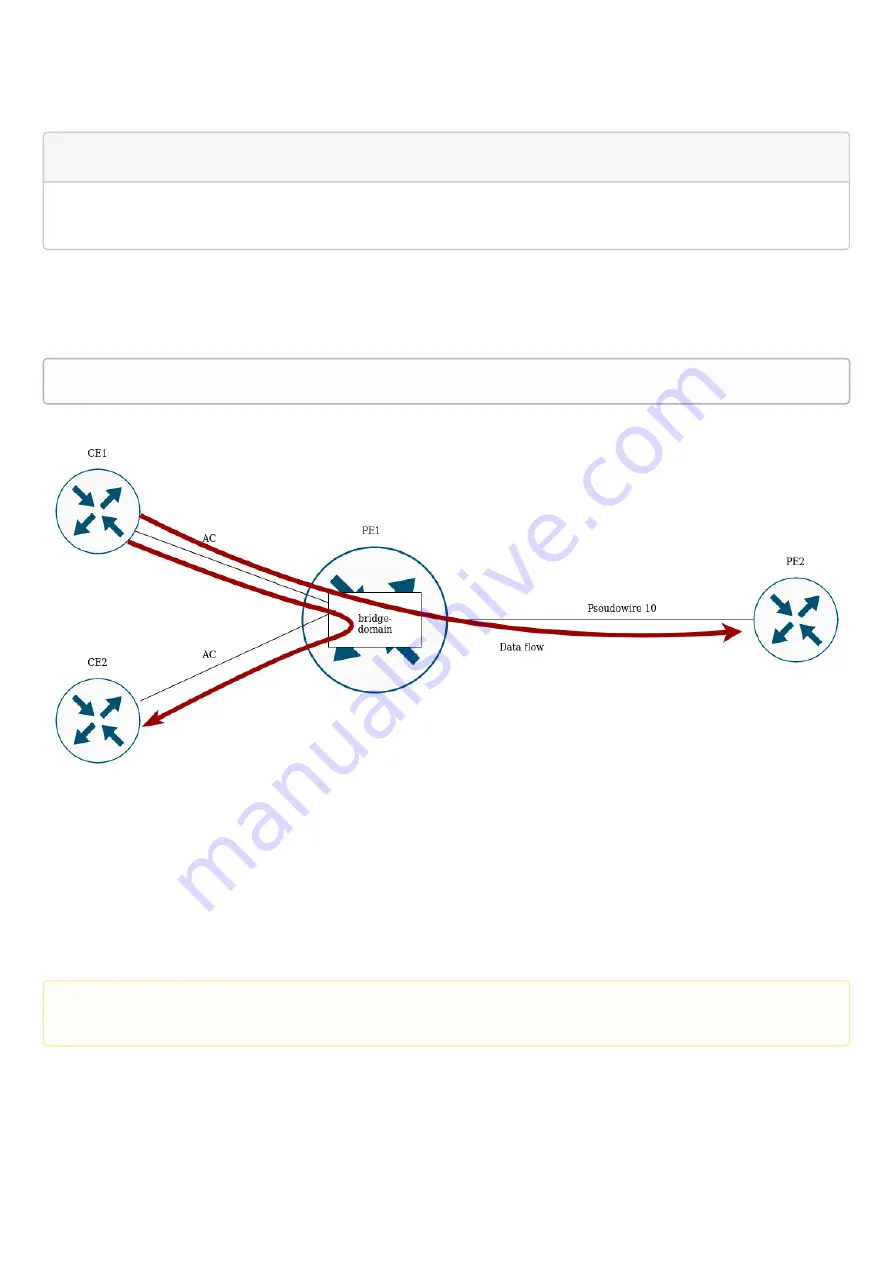
12.9 Operation with the bridge domain within MPLS
To organize L2VPN service, you need to configure a bridge domain on the device, create the required AC, PW
(LDP-signaling) and include all the necessary elements in this bridge domain.
Traffic is switched between elements of the bridge domain based on the listed rules:
A MAC address table is automatically created for each bridge domain, similar to Ethernet switches.
Ethernet frames are switched based on analysis of the destination MAC address (DST MAC).
Frames with a known DST MAC will be sent to the appropriate AC/PW.
Frames with unknown DST MAC, broadcast- and multicast-frames (so called BUM traffic, "Broadcast,
Unknown unicast and Multicast") will be sent to all elements of the bridge domain, except for the
element (AC or PW) from which you entered the bridge domain.
Switching takes into account the DST MAC in the frames, but does not take into account the VLAN tags
present on the frames — thus, switching within a bridge domain is not "VLAN-aware".
The bridge domain can operate in two transport modes: ethernet or vlan. Transport mode sets the rules for
handling traffic to and from the bridge domain.
In LDP signaling, ethernet mode (Raw mode, type 5) is used by default. A transport mode can be set for each
individual VPLS instance.
For point-to-point, a bridge domain is created automatically.
In the current implementation, the bridge domain does not allow traffic of data link layer protocols
such as STP, LLDP, CDP, etc.















































