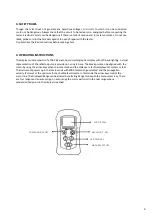
Operates key
Power on/off key
Switch on and off the unit. The unit have auto
powering down If the key is not depressed 5 minutes
Menu select key
This allows the setting up of the Propagation Velocity Factor, Cursor
Control, Range select and Measure unit via the up-down arrow keys.
Backlight key
This illuminates backlight to the display when depressed.
Down key
The down key reduces the Propagation Velocity
Factor, scrolls the cursor left, scrolls down through the
Ranges and toggles measure unit between Metres
and Feet with the appropriate menu selected.
When the Locate Mode is selected and the key pressed twice and then held the
cursor scrolls at a faster rate than normal in the direction indicated.
Up key
The Up key increases the Propagation Velocity Factor, scrolls the
Cursor right, scrolls up through the Ranges and toggles measure unit
between Metres and Feet with the appropriate mode selected.
When the Locate Mode is selected and the key pressed twice and then held the
cursor scrolls at a faster rate than normal in the direction indicated
.
4.1 FAULT LOCATION
The following general points should be observed when checking a faulty cable:
(1) Carry out the safety checks listed under the SAFETY RULES.
(2) The instrument measures the length of cable, not the length of the cable path.
Buried cable loops, snaking cables and other irregularities need to be taken into account.
(3) Measurements will be greater on wet cables.
(4) Do not connect the instrument to a cable pair that is to be ‘burned’ with a breakdown test set.
3.