Mechanical Operations and Maintenance Manual for Industrial Robot ER10-3(4)-900
Chapter Five Common Faults and Treatment Measures
When the robot body fails, please refer to this chapter for initial fault diagnosis. The conditions listed
below cover the common faults that may occur on the robot body, the analysis of the fault causes, and the
corresponding handling measures, which can help users to troubleshoot common faults.
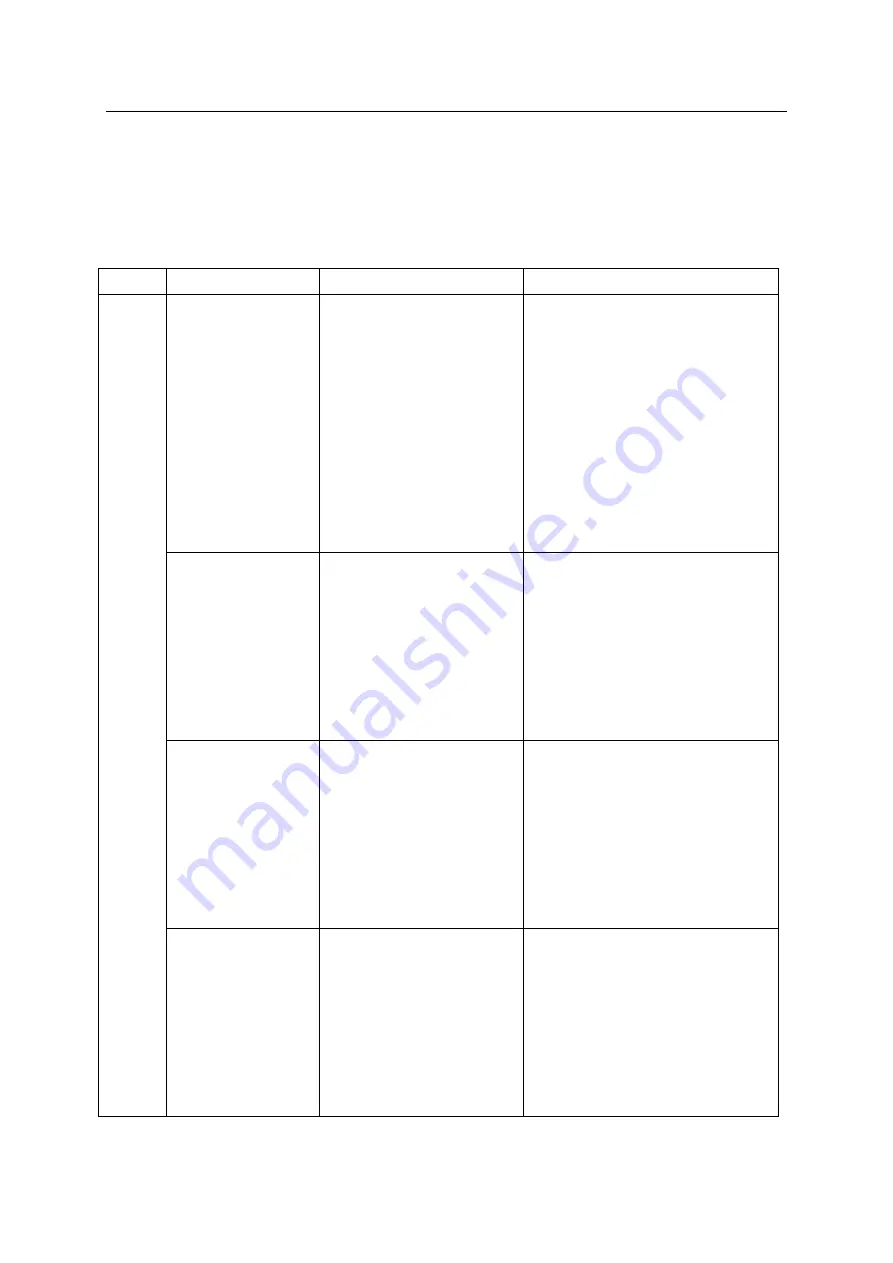
Fault
Fault classification
Possible cause of fault
Treatment measures
Vibratio
n
and
abnorm
al noise
The base and the
mounting base are not
firmly fixed
(1)
The flatness of the base
and the installation base is not
enough, or foreign matter is
included, which makes it
unable to fit tightly during
installation;
(2)
When connecting the base
and the installation base, the
screws are not tightened, or the
screws
are
loose
after
long-term operation.
(1)
Check and trim the flatness of the
base and the installation base to make
the tolerance meet the installation
requirements;
( 2 )
If there is a foreign object
between the base and the installation
base, please clean it and reinstall it
firmly;
(3)
When tightening the screws, use a
torque wrench to tighten with the
required torque.
The mounting base
and the foundation are
not firmly fixed
( 1 )
The ground installation
conditions do not meet the
requirements,
resulting
in
insufficient
foundation
rigidity;
( 2 )
The specifications and
strength of chemical bolts do
not meet the requirements.
Refer to the "3.2.3 Ground Installation"
section of this manual to make the
concrete foundation and chemical bolt
set meet the installation requirements.
The robot vibrates
obviously in a certain
posture or state
( 1 )
The load exceeds the
allowable value, resulting in
insufficient stiffness in a
specific posture, resulting in
vibration;
( 2 )
Improper operating
procedures
and
parameter
settings can cause vibration.
(1)
Reduce the load and ensure it is
within the allowable range;
(2)
Modify the program and adjust the
parameters, step by step from low
speed to high speed, until the robot's
action status returns to normal.
The vibration and
abnormal noise of the
robot in the following
three situations:
( 1 )
After the
collision;
( 2 )
Long-term
overload operation;
These three conditions will
cause damage to internal
components (gears, bearings,
reducers, etc.), resulting in
vibration and abnormal noise.
( 1 )
Check each axis of the
single-action robot, and consult the
after-sales service department of our
company
for
replacement
after
confirming the damaged joint;
(2)
In the later operation process, try
to avoid collision and long-term
overload operation, and regularly








































