DIGITAL YACHT LTD
NavLink Quick Start Guide
Condition
Red LED
Yellow LED
Green LED
ON (Solid)
TCP Link
Established
Fast Blink
No Wireless
Connections
Data
No Data Link
Slow Blink
Wireless
Connection
Established
Data
UDP Link
Established
OFF
No Data
No Power
Installation Step 4
– Wireless Interfacing
The NAVLINK receiver has an integrated 802.11b+g wireless adaptor which creates a wireless hotspot on-board
your boat. The SSID
(name) of the wireless hotspot that NAVLINK creates will be “DY-NavLink-xxxx” where xxxx
is a four digit code unique to your NAVLINK.
To connect to NAVLINK, simply scan for wireless hotspots on your wireless device. The exact procedure will vary
from device to device so consult the user manual for your device to understand how to connect to a wireless
hotspot.
The NAVLINK uses TCP or UDP protocol to transmit serial NMEA data and it is important that the program or
application on the wireless device supports data reception via TCP or UDP in order to work correctly. Your choice
of which protocol to use will probably be dictated by what protocols your navigation app can receive.
TCP is a single device to device protocol and only one mobile device may communicate with the NAVLINK via
TCP at a time. You will be able to connect multiple wireless devices to the NAVLINK but only one of the devices
will be able to receive TCP data.
UDP is a single device to multiple device protocol and allows multiple mobile devices to all receive the same data.
If your navigation app supports both TCP and UDP, then UDP is probably the better of the two protocols to use.
Once you have wirelessly connected your mobile device to the NAVLINK, you will need to run the Application on
your mobile device that accepts NMEA data over a TPC or UDP connection. For TCP you need to enter the IP
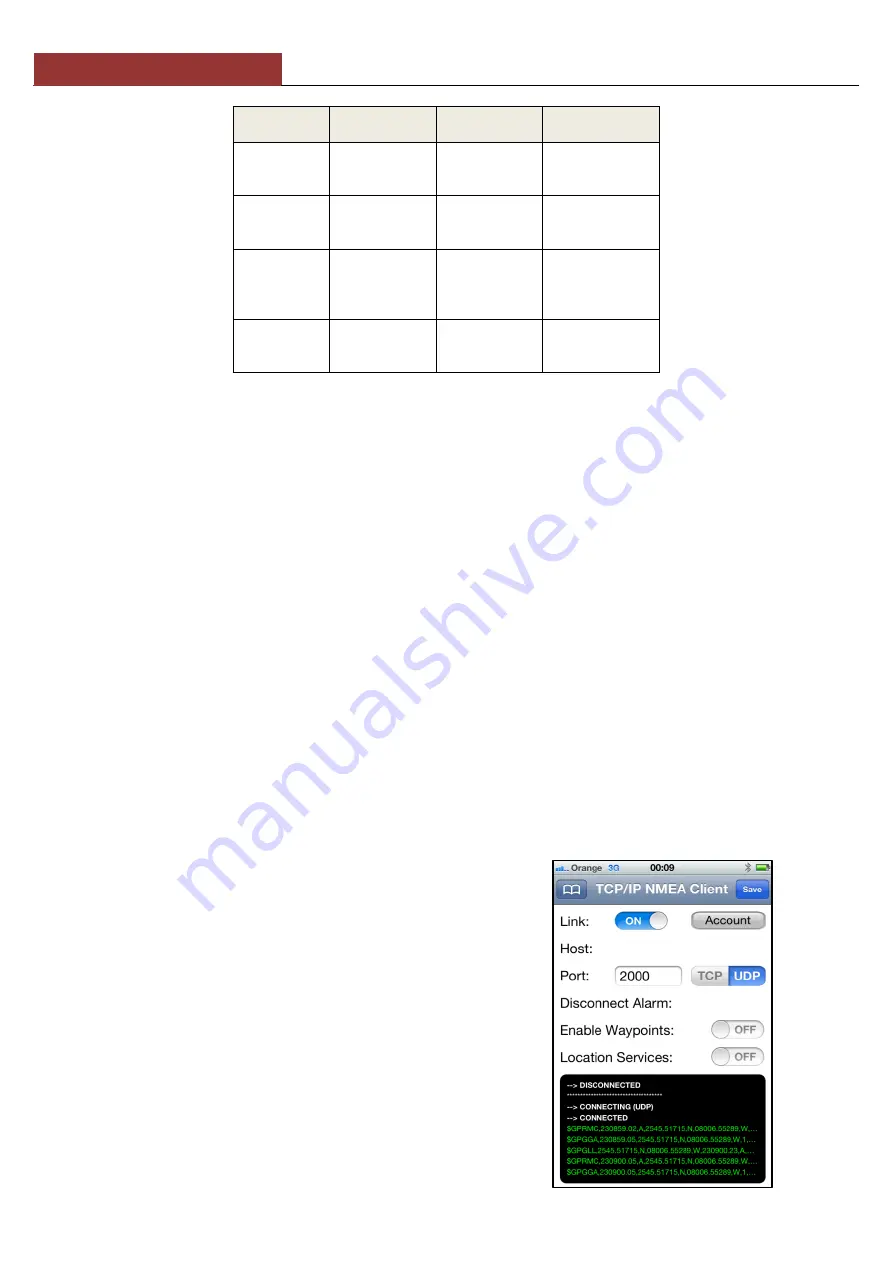
address and port that NAVLINK transmits data on as shown below and for UDP you just enter the port number;
IP Address
-
192.168.1.1
Port
-
2000
You should now be able to receive data wirelessly from the
NAVLINK.
The data that the NAVLINK outputs is standard NMEA0183
and some apps (such as our free iAIS app) will display the
raw data, which is a good method of testing the system is
working.
The screen shot in Fig 1, is from our iAIS app and shows the
NMEA0183 data being received in the black terminal window.
Figure 1




