Initial Startup
25
Cat. No. 01022940
Normal Operation
During normal operation, the system usually will start up and shut down based on signals from a level control or pressure
switch. Adjust the feed pressure as required (no higher than 150 psig) to maintain a constant product flow. Record the
performance data regularly and compare it to the performance on initial start up. If any changes are noticed, the product
flow should be normalized to determine if cleaning is required (see “Product Flow Calculations”).
Product Flow Calculations
The product flow rate depends primarily on feed water pressure, product water pressure, and temperature. All Series E
and M units have specified nominal flow rates based on approximately 105 psig net pressure and 77°F temperature. How-
ever, in most applications the temperature and pressure are lower, so the product flow rate is lower than the nominal flow
rate. The actual flow rate must be converted to flow under standard conditions, then compared to the initial performance
(also converted to standard conditions) to determine whether the system is still working properly.
To convert the data to standard conditions,
1. Measure the product flow. Example: 1000 ml/min
2. Measure the feed pressure. Example: 120 psig
3. Measure the product pressure. Example: 5 psig
4. Subtract the product pressure from the feed pressure. Example: 115 psig
5. Divide the product flow by the result from step 4. Example: 1000 ÷ 115 = 8.69 ml/min/psi
6. Multiply the result from step 5 by 105. Example: 8.69 x 105 = 913 ml/min
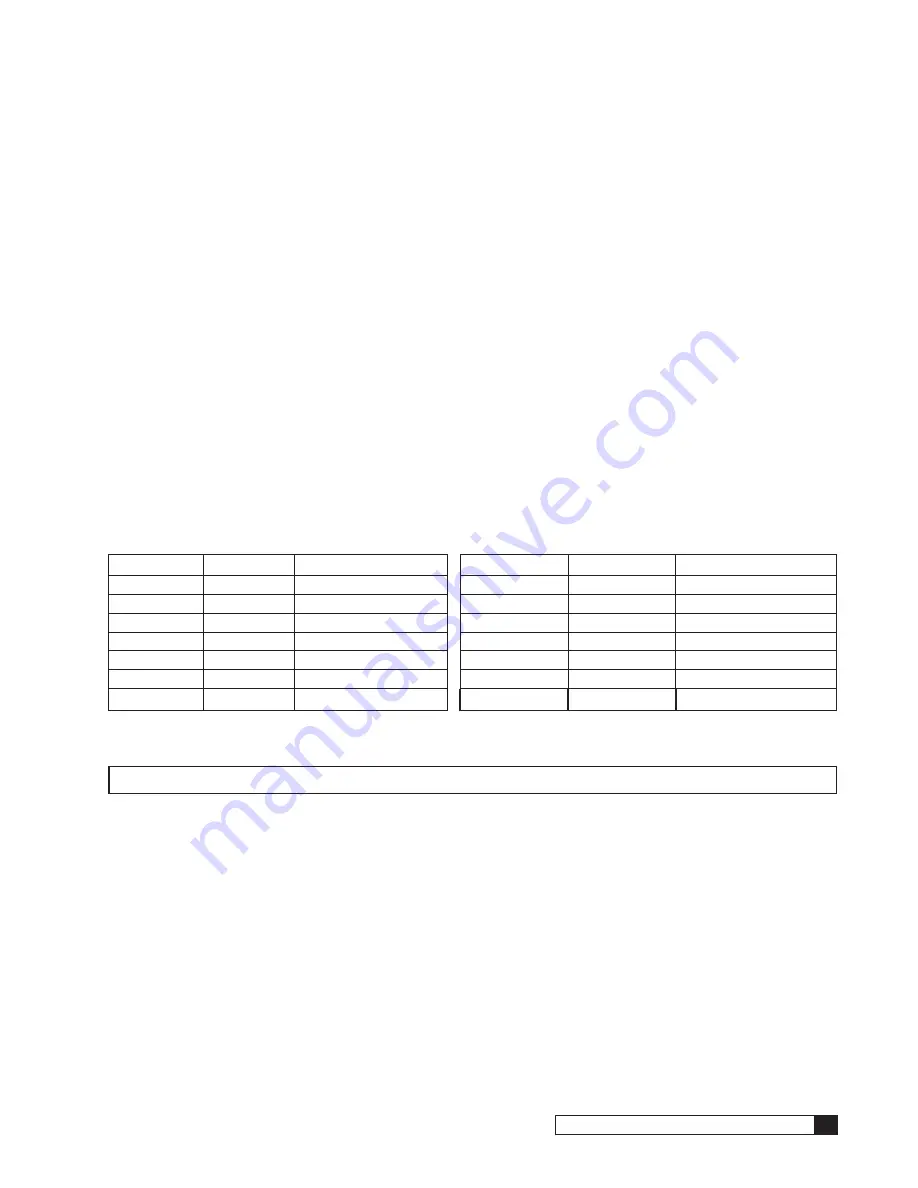
7. Measure the temperature of the feed water, then determine the temperature correction factor from Table 1.
Example: At a temperature of 55°F , the factor is 1.54.
Temp. °F Temp. °C Correction Factor
Temp. °F
Temp. °C
Correction Factor
40
4.4
2.12
75
24
1.04
45
6.7
1.90
80
27
0.95
50
10
1.71
85
29
0.86
55
13
1.54
90
32
0.79
60
16
1.39
95
35
0.72
65
18
1.26
100
38
0.66
70
21
1.14
Table 1. Temperature Correction Factors
8. Multiply the result of step 6 by the temperature correction factor. Example: 913 ml/min x 1.54 = 1406 ml/min.
NOTICE
To convert ml/min to gallons per day, multiply by 0.38. For example, 1406 ml/min x 0.38 = 534 gpd.
9. Compare the current standardized flow to the initial standardized flow. If the flow has decreased by 15% or
more, it is time to clean the elements.
Example: If the initial standardized flow was 570 gpd, and the current standardized flow is 470 gpd, the flow has
decreased by 100 gpd, or 18% (100/570) = 0.18. The elements should be cleaned.
10. If the problem cannot be corrected with the troubleshooting guide and assistance is required, please have the
following information available when calling the Culligan dealer:
•
Product flow rate
•
Concentrate flow rate
•
Feed pressure
•
Product water quality
•
Feed water quality
•
Feed water temperature
•
Prefilter outlet (and inlet if the optional prefilter inlet gauge was installed)
•
Product pressure
Summary of Contents for M1 Series
Page 83: ...Notes 79 Cat No 01022940 Notes ...
Page 84: ......
















































