W
HITE
P
APER
(cont.)
4
Doc Number
TC000602WP
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
.
In contrast, a SAN is a high-performance network that can handle intense messaging efficiently.
The efficiency of SANs allows data to be distributed anywhere within the cluster, which increases
scalability through greater parallelism and higher availability. Initially, only proprietary SAN
technologies could handle the large amount of messaging traffic in a cluster. Therefore, in
December 1997, Compaq, Intel, Microsoft and other industry leaders developed the Virtual
Interface (VI) Architecture specification to promote an industry-standard architecture for server-to-
server communication.
1
Unlike traditional networking technologies, the VI Architecture allows
distributed applications to move data between clustered servers without invoking operating system
functions. As a result, operating systems perform significantly better by avoiding unnecessary
transitions to and from user applications and by avoiding excessive CPU interrupts.
Relational database, operating system, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) products were
among the first to leverage affordable VI Architecture technology to add robustness and
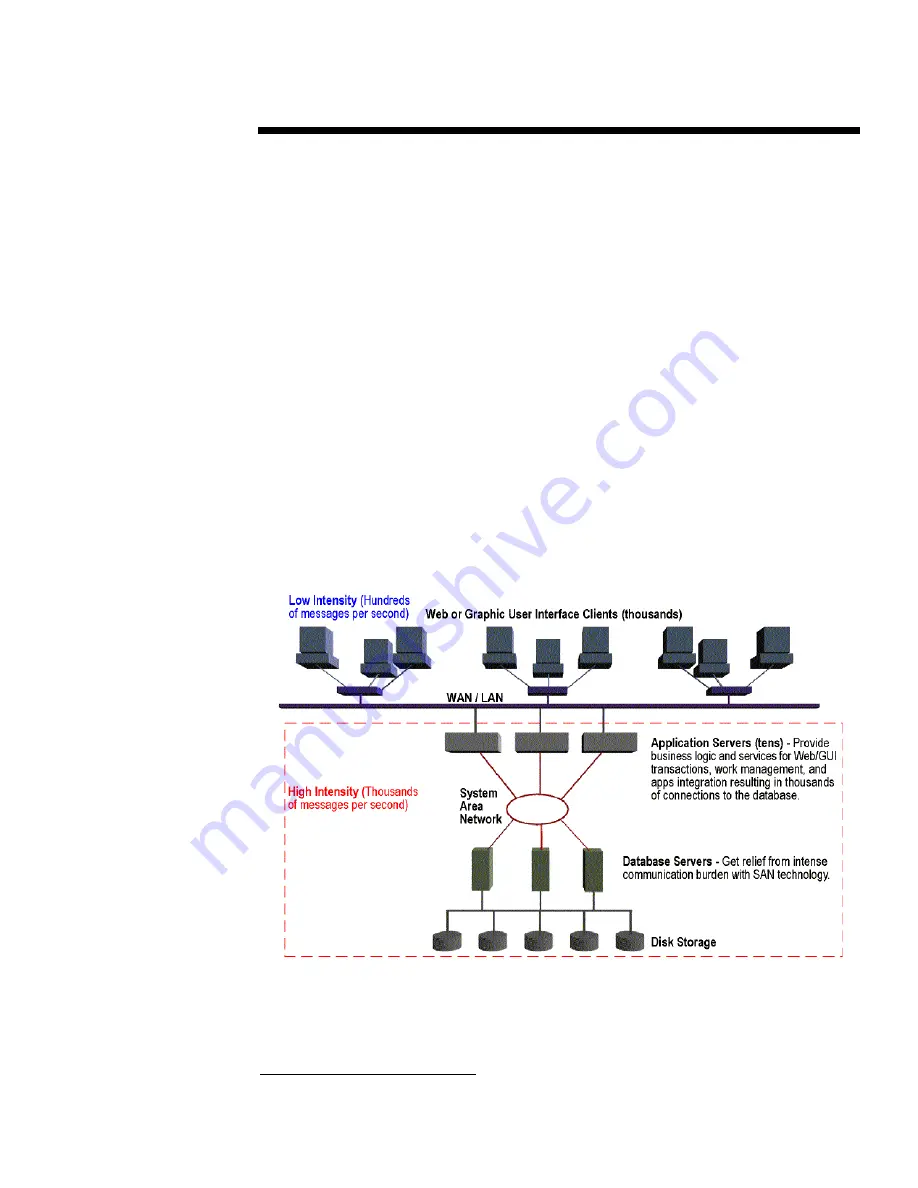
predictability to industry-standard clusters. ERP applications are configured using multiple tiers to
achieve sufficient scale (see Figure 1). The top tier consists of the ERP web or graphic user
interface, the middle tier contains application servers, and the bottom tier contains relational
database servers. ERP applications place great communications demands on the database servers,
resulting in intense messaging. Message intensity within the server cluster is one to two orders of
magnitude greater than WAN/LAN [or wireless] messaging destined outside the cluster.
Request/reply transactions consisting of SQL requests and SQL result-sets (messages to and from
the database) account for most of the messaging traffic. Recent large SAP sales and distribution
benchmarks require the database to manage message profiles exceeding 32,000 messages per
second with an average message size just over 1,600 bytes.
Figure 1. Multi-tier architecture.
1
For more information, see technology brief
Virtual Interface Architecture for System Area Networks
, document number
0184-0699-A.









