14 www.clearone.com
Notch Filter
•
. A band-stop filter that can remove a select range of frequencies. Commonly used for removing
specific resonant frequencies from a system.
Parametric equalizer
•
. A multi-band variable equalizer that allows the user to define the amplitude of the filter,
shift the center frequency of the filter, and control how wide the range is to which the equalizer is applied.
filters are configured and adjusted using Converge Console software.
Crossovers
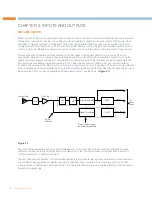
The Converge Pro 880/840T features a crossover that combines high-pass and low-pass filters to divide a full-range
signal into separate frequency ranges. These ranges can then be sent to amplifiers and loudspeakers optimized for
producing those respective frequency ranges
for example, the bottom end of a frequency range might be defined as 400Hz and lower. This signal might then be
heavily compressed and sent to bass bins and woofers powered by amplifiers. The midrange (say, 400Hz to 5kHz)
can be sent to full-range loudspeakers. The high end (say, 5kHz and above) can be directed to smaller amplifiers and
associated tweeters, piezos, horns, etc.
Converge Pro audio conferencing devices include three types of crossovers: butterworth, bessel, and linkwitz-Riley.
each crossover is characterized by the steepness of their roll-off slopes (the rate of attenuation outside their passbands).
Crossovers in the Converge Pro are created by assigning the appropriate type of high-pass filter in a processing block
with the complementary low-pass filter in a separate processing block.
bessel Crossover
•
. Utilizes a low-pass filter design with a linear phase response (or maximally flat phase
response), and a monotonic decreasing passband amplitude response (it rolls off at DC and continues
throughout the passband). linear phase response (a linear phase shift vs. a frequency producing a straight line)
results in constant time delay for all frequencies within the passband. The linear phase shift reproduces a near-
perfect step response (with no overshoot or ringing resulting from a sudden transition between signal levels). The
drawback is a sluggish roll-off rate. for example, for the same circuit complexity, the response for a butterworth
crossover rolls off nearly three times as rapidly.
butterworth Crossover (1 pole)
•
. A low-pass filter design characterized by a maximally flat magnitude response
(i.e., no amplitude ripple in the passband).
Linkwitz-riley (Lr-4) Crossover (2 poles)
•
. The 4th-order (24db/octave slope) linkwitz-Riley (lR-4) design
represents a vast improvement over the previous 3rd-order (18db/octave) butterworth standard. It consists of a
cascaded 2nd-order butterworth low-pass filter, and is considered the de facto standard for professional active
audio crossovers.
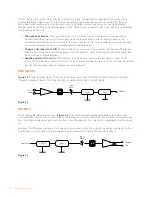
Converge Pro has an intuitive filter display, which shows the aggregate filter response for a particular processing block.
This display can overlay the filter responses of other processing blocks, which is useful in designing active crossovers.
The aggregate phase response of the processing block can also be shown superimposed on the filter response curve.
CLeArONe’s DAre™ FeeDbACk eLimiNATOr
Why automatic feedback elimination?
Any audio system that amplifies the audio signal picked up by a microphone via loudspeakers in the same space is
vulnerable to feedback. These annoying screeches and howls can occur when the audio from the loudspeaker is
picked-up by a microphone and re-amplified repeatedly.
Getting a sound reinforcement system to reach its theoretical ptential gain will likely require system equalization. Part of
the equalization precess uses narrow-band filters to decrease offending feedback ring mode levels. feedback happens
at a specific frequency; therefore, filters with narrow bandwidth (Q) can be used to reduce the level of the audio system
at the feedback frequency.