33-11
Catalyst 2975 Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-19720-02
Chapter 33 Configuring QoS
Understanding QoS
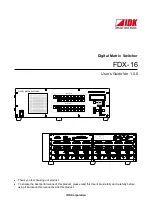
shows the policing and marking process.
Figure 33-4
Policing and Marking Flowchart on Physical Ports
Mapping Tables
During QoS processing, the switch represents the priority of all traffic (including non-IP traffic) with an
QoS label based on the DSCP or CoS value from the classification stage:
•
During classification, QoS uses configurable mapping tables to derive a corresponding DSCP or
CoS value from a received CoS, DSCP, or IP precedence value. These maps include the
CoS-to-DSCP map and the IP-precedence-to-DSCP map. You configure these maps by using the
mls
qos map cos-dscp
and the
mls qos map ip-prec-dscp
global configuration commands.
On an ingress port configured in the DSCP-trusted state, if the DSCP values are different between
the QoS domains, you can apply the configurable DSCP-to-DSCP-mutation map to the port that is
on the boundary between the two QoS domains. You configure this map by using the
mls qos map
dscp-mutation
global configuration command.
•
During policing, QoS can assign another DSCP value to an IP or a non-IP packet (if the packet is
out of profile and the policer specifies a marked-down value). This configurable map is called the
policed-DSCP map. You configure this map by using the
mls qos map policed-dscp
global
configuration command.
86835
Yes
Yes
No
No
Pass
through
Drop
Mark
Get the clasification
result for the packet.
Is a policer configured
for this packet?
Check if the packet is in
profile by querying the policer.
Check out-of-profile action
configured for this policer.
Drop packet.
Modify DSCP according to the
policed-DSCP map. Generate
a new QoS label.
Start
Done