12-27
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Chapter 12 Configuring Mobility GroupsWireless Device Access
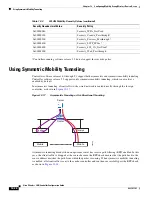
Using Symmetric Mobility Tunneling
Figure 12-18
Symmetric Mobility Tunneling or Bi-Directional Tunneling
Symmetric mobility tunneling is also useful in the following situations:
•
If a firewall installation in the client packet path drops packets because the source IP address does
not match the subnet on which the packets are received.
•
If the access-point group VLAN on the anchor controller is different than the WLAN interface
VLAN on the foreign controller. In this case, client traffic could be sent on an incorrect VLAN
during mobility events.
Note
Although a 2100 series controller cannot be designated as an anchor for a WLAN when you are using
auto-anchor mobility, it can serve as an anchor in symmetric mobility tunneling to process and forward
the upstream client data traffic tunneled from the foreign controller.
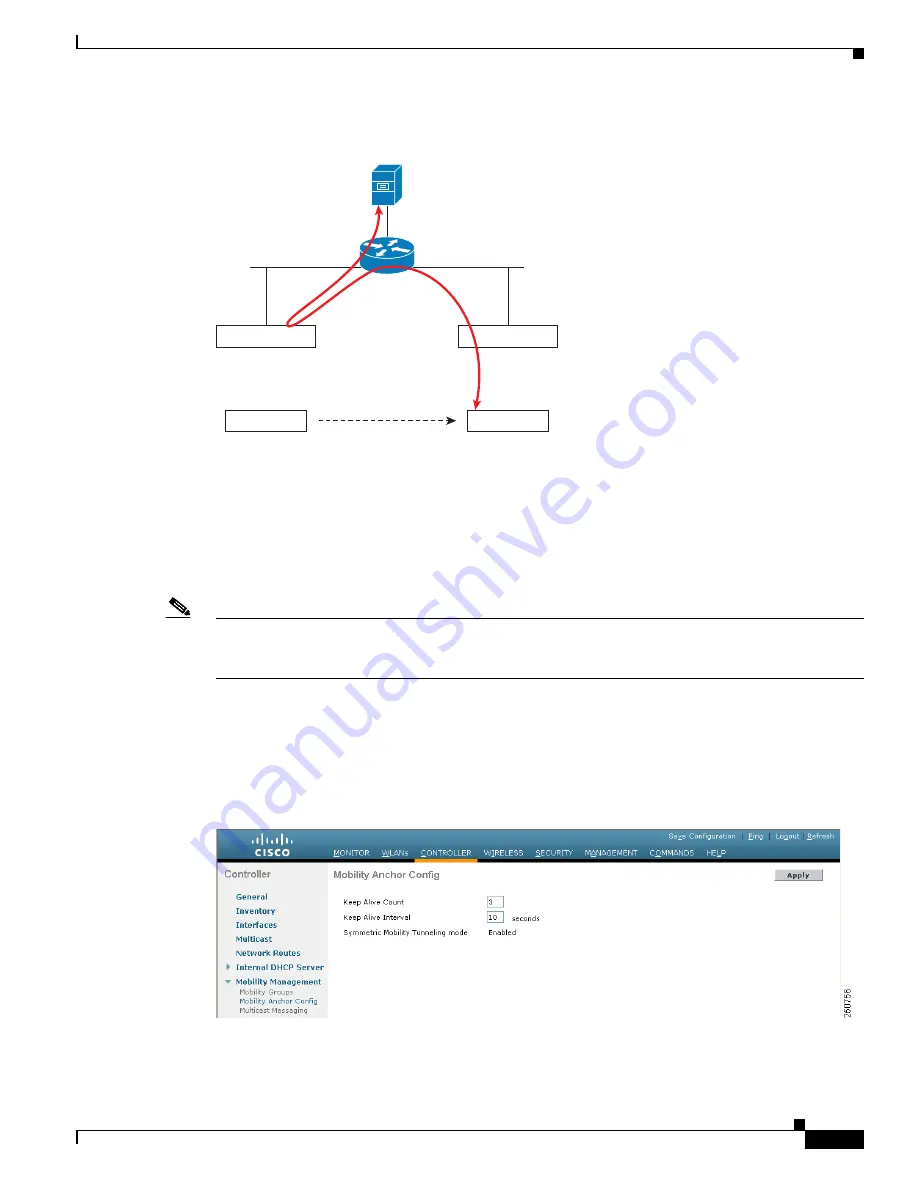
Both the controller GUI and CLI show that symmetric mobility tunneling is enabled on the controller:
•
To use the controller GUI to verify that symmetric mobility tunneling is enabled, click
Controller
>
Mobility Management
>
Mobility Anchor Config
to open the Mobility Anchor Config page (see
). The Symmetric Mobility Tunneling Mode field shows Enabled.
Figure 12-19
Mobility Anchor Config Page
Router
with RPF
Server
Static Anchor
Foreign
Mobile
Mobile
210952