Indications and Contradictions
The deep penetration of the device can reduce pain from joint sprains, bursitis,
muscle cramps, neuralgia and other musculoskeletal disorders in a short period
of time. Almost all soft tissue diseases are associated with trauma, excessive
muscle use or abnormal posture, and most of the scar tissues involved in these
diseases can be treated with this device. Avoid excessive stress and prolonged
physiotherapy when using the device. Also avoid sensitive areas such as head,
face and cervical vertebrae. Stop physiotherapy if there is inflammation, swelling
or increased pain.
The ongoing research is about the impact of vibration training on specific medical
conditions.
This is very likely to reduce the types of contradictions mentioned above, and
practical experience has shown that in many cases , it is also a physiotherapy
recommendation to combine vibration training into physiotherapy programs.
This must be done by, or in the company of, a doctor, expert or physical
therapist.
Indications
Contradictions
>Pain and cramps due to
muscle injury, sprains, strains
>Help the flow of edema fluid in
the swollen area
>Relax thickened connective
tissues and fascias
>Reduce the accumulation of
lactic acid in muscles
>Increase joint mobility
Eliminate muscle fatigue
>Aneurysm, bleeding, use of blood
thinner
>Heart disease, with a pacemaker
or defibrillator
>Pregnancy, cancer
>Withing 90 days of intra-articular
fixation, the device should not be
used withing 3 inches of internal
fixation.
>Sensitive area: head, face, cervical
vertebrae, spine
>Positions close to the bones with
less muscle coverage: tibia, the
back of the foot, the back of the
hand
Use method
Operation Program of Lower
Limbs
Prone position
Small flat head vertically
downward
Hamstring
Biceps femoris 20s-30sx3 times
Semitendinosus 20s-30sx3 times
Semimembranosus 20s-30sx3
times
The movement direction is from
up to down.
Small flat head outward 45
°
Gracilis 10s-15sx2 times
Adductor longus
10s-15sx2 times
Adductor brevis 10s-15sx2 times
Triceps surae
Gastrocnemius 20s-30sx3 times
Soleus 20s-30sx3 times
The movement direction is from
up to down.
Small round head vertically
downward
Popliteus
Knee straightening position 15s-
30s
Knee bending position 15s-30s
Supine position
Small flat head vertically
downward
Quadriceps femoris
Rectus femoris 30s-45sx2 times
Vastus lateralis 30s-45sx2 times
Vastus medialis 30s-45sx2 times
Vastus intermedius 30s-45sx2
times
The movement direction is from
up to down.
The patient slowly and slightly
bends the knee.
Small flat head vertically
downward
Sartorius 30s-45s
Tensor fasciae latae 15s-20sx2
times
Tibialis anterior 15s-20sx2 times
Peroneus longus 15s-20sx2 times
Peroneus brevis 15s-20sx2 times
The movement direction is from
up to down.
Use Method
Gonarthritis
Supine position
Small head vertically downward
Quadriceps femoris
Rectus femoris 30s-45sx2 times
Vastus lateralis 30s-45sx2 times
Vastus medialis 30s-45sx2 times
Vastus intermedius 30s-45sx2 times
The movement direction is from up to
down.
The patient is slowly and slightly
bending the knee.
Small round head vertically
downward
Iliac bone edge
–
iliac bone anterior
30s-1min
Rectus femoris, inguen 1min
Tensor fasciae latae 15s-20sx2 times
Patellar ligament area 20sx3 times
Prone position
Small round head vertically downward
Popliteus 30s-45s
Knee straightening position 15s-30s
Knee bending position 15s-30s
Triceps surae
Gastrocnemius 20s 30sx3 times
Soleus 30s-45sx2 times
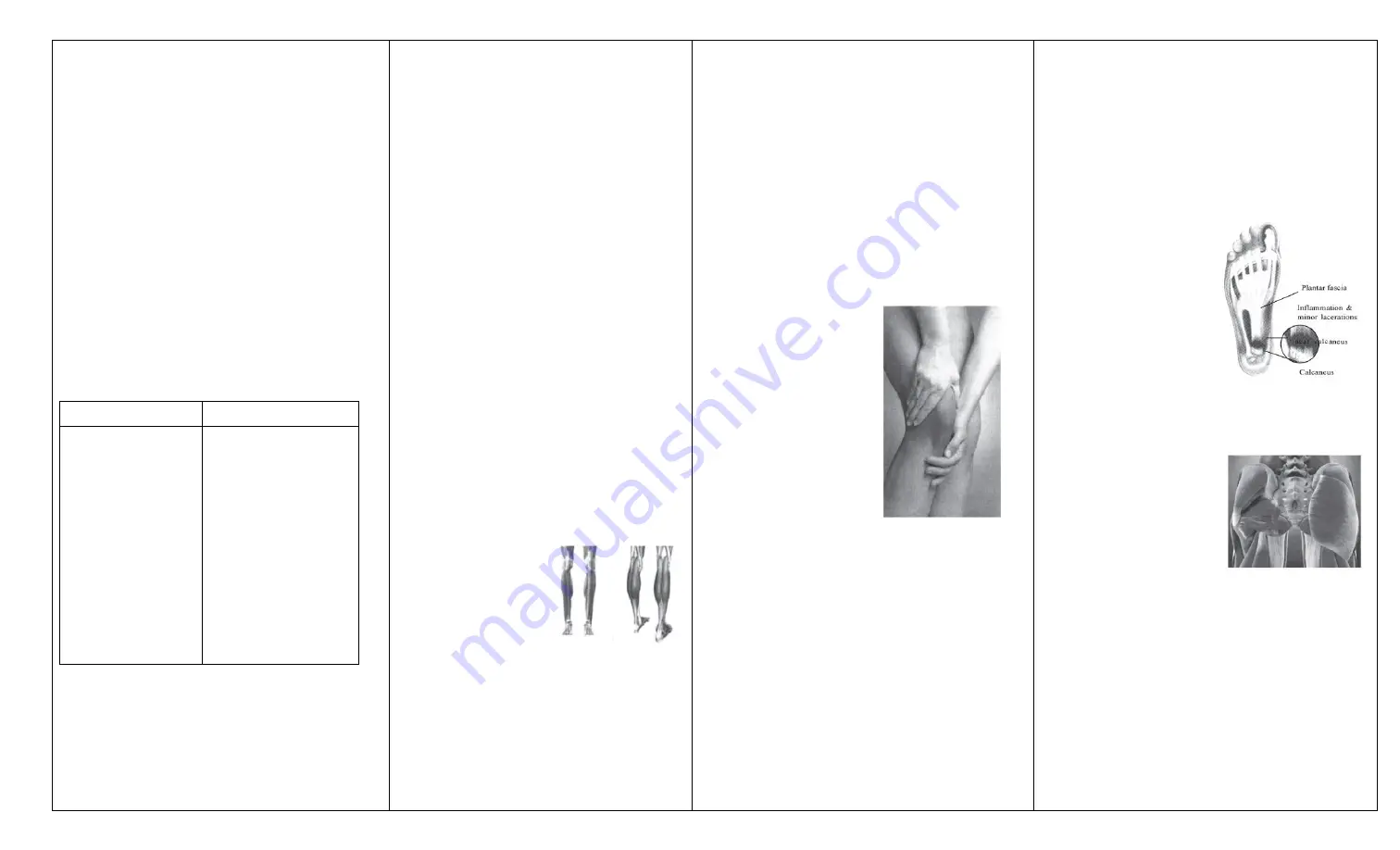
Plantar fasciitis
Prone position (single side)
Small flat head vertically downward:
Hamstring
Biceps femoris 20s-30sx3 times
Semitendinosus 20s-30sx3 times
Semimembranosus 20s-30sx3 times
The movement direction is from up to
down.
U head vertically downward
Popliteus
Knee straightening position 15s-30s
Knee bending position 15s-30s
Triceps surae
Gastrocnemius 20s-30sx3 times
Soleus 20s-30sx3 times
The front foot sole touches the ground.
Small round head vertical to planta
pedis:
Plantar fascia
Operation Program of Sacroiliac Part
Prone position (single side)
Small flat head vertically downward:
Glutues medius 30s-1minx4 times
Glutues maximus 30s-1minx4 times
Piriformis 1min-1.5 min
Articulatio sacroiliaca 1min-1.5 min
The direction is from inside up to
outside down, along the muscular
direction.
Hamstring
Biceps femoris 20s-30sx3 times
Semitendinosus 20s-30sx3 times
Semimembranosus 20s-30sx3 times
From up to down
Supine position
Tibialis anterior 15s-20sx2 times
Peroneus longus 15s-20sx2 times
Peroneus brevis 15s-20sx2 times
The movement directions is from up to
down.





















