Maintenance • 51
T E L E S C O P E M A I N T E N A N C E
After you have set up your telescope and started using it, there are a few things to
remember for future reference.
To minimize the need to clean your telescope, replace all lens covers once you
have finished using it. Since the front of the telescope tube is open
ALWAYS
replace the front cover when the telescope is not in use. This will minimize the
amount of contaminants from entering the optical tube and minimize the number
of times your telescope needs to be cleaned.
The long tube of your Newtonian telescope acts as a dew shield to prevent moisture
from building up on the primary mirror. However, on extremely damp nights, the
tube may only slow the formation of dew on the primary mirror. If dew condenses
on the primary mirror it can be removed with a hair dryer or by pointing the tele-
scope at the ground.
Occasionally, dust and/or moisture may build up on the primary mirror of your
telescope. Special care should be taken when cleaning any optical instrument so as
not to damage the optics. Internal adjustments and cleaning should be done only
by the Celestron repair department. If your telescope is in need of internal
cleaning, please call the Celestron repair department for specific information on
service.
Exact mirror alignment (i.e., collimation) of a fast f-number Newtonian reflector is
necessary in order to obtain the best optical image quality possible. Although your
telescope was fully collimated at the factory, you should check collimation to
ensure that rough handling has not altered the alignment of the mirrors.
To determine whether or not recollimation is necessary, the telescope should be
set up outside at night. It should be a still night and one in which you have let the
telescope sit outside for 30 to 45 minutes before attempting collimation. You
should also wait for a night with good seeing conditions and avoid looking over
anything that produces heat waves (i.e., roof tops, car hoods, etc.).
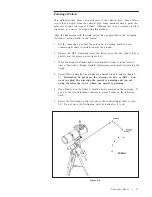
Pick a bright star and center it in the field of the telescope. Study the image of the
star while racking it in and out of focus using 30 to 60 power for every inch of
aperture. For your G-8N this equates to about 240 to 480 power and for the C150-
HD is about 180 to 360 power.. If an unsymmetrical focus pattern is present, then it
may be possible to correct this by recollimating only the primary mirror. Simply
removing the ocular during the daytime and looking down the focus tube is
NOT
a
satisfactory way of determining collimation. Read the procedural instructions
through completely
BEFORE
attempting!
To star collimate, the telescope should be on either a motor driven (i.e., tracking)
equatorial mount that is approximately polar aligned or pointed at a stationary star
without the motor drive running. Polaris, the North Star, is the perfect collima-
tion star for northern hemisphere observers since it appears motionless against the
background sky long enough to perform the collimation procedure. Polaris is the
last star in the handle of the Little Dipper (Ursa Minor) and its distance above the
northern horizon is always equal to your latitude angle.
Collimation
Care and Cleaning
of the Optics