24
suspension
glossary
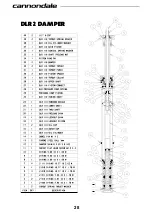
Damping
- The process of dissipating energy
and slowing down the suspension motion.
Damping absorbs the force of a bump or
landing. Damping is usually done with oil,
but can be done with air and friction as well.
Spring
- The part of a suspension fork or
shock that holds the rider/bike up. Springs
can be metal coils (steel or titanium) or high
pressure air.
Compression
- The process of squeezing
together. The front and rear suspension
compress when hitting a bump, landing off
a jump, or braking for corners. Compression
can refer to the spring or damping
(compression damping).
Rebound
- The process of extending back
from a compressed state. The front and rear
suspension rebound after being compressed
from a bump or jump landing. Rebound can
refer to the spring or damping (rebound
damping).
Low Speed (compression or rebound)
- Low
speed damping references the speed at
which the fork/damper travels through its
stroke. It does NOT refer to the speed at which
the rider is moving. Low speed bumps are
typically round in shape or smooth actions
like jump landings and pedal bob. In the
case of rebound, it mostly refers to rebound
speed caused by smaller bumps where the
fork does not get fully compressed.
High Speed (compression or rebound)
-
High speed damping references the speed
at which the fork/damper travels through
its stroke. It does NOT refer to the speed at
which the rider is moving. High speed bumps
are typically square in shape or harsh terrain
like sharp-edged rocks that may cause pinch
flats. In the case of rebound, it mostly refers
to rebound speed caused by larger bumps
where the fork gets fully compressed.
Bottom Out
- When the front or rear
suspension fully compresses to absorb a
bump or jump landing. A hard stop is usually
felt at bottom out.
Top Out
- When the front or rear suspension
fully extends after absorbing a bump or jump
landing. A soft stop is usually felt at top out.
The fork and shock are typically topped out
without a rider on the bike.
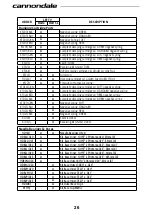
Compression Adjuster
- Used to adjust the
front or rear compression damping setting.
Rebound Adjuster
- Used to adjust the front
and rear rebound setting
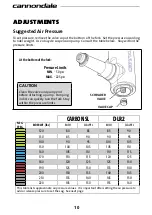
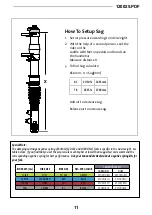
Sag
- Refers to how much the front and rear
suspension compress when a rider sits on
the bike. Sag is measured as a percentage
of suspension travel. Typical sag values are:
20-30% for XC riding and 25-35% for Trail/
Freeride.
Preload
- Refers to how much initial
compression is applied to a spring. In the
case of an air spring, preload is achieved by
increasing the air pressure. You use preload
to adjust the sag. More preload decreases
the sag. Less preload increases the sag.
Spring Rate
- Refers to the strength of a
spring. A spring with a higher rate is stiffer, a
lower rate softer.
Diving
- When a suspension fork compresses
and causes the pitch of the bicycle drop.
Mostly occurs when braking.
Revalve
- Revalving is the process of changing
the internal compression and rebound shims
to change the flow of oil through passages in
the forks and shock. A suspension specialist
should revalve your bike’s suspension.