Appendix B. Installation Scenarios
B-5
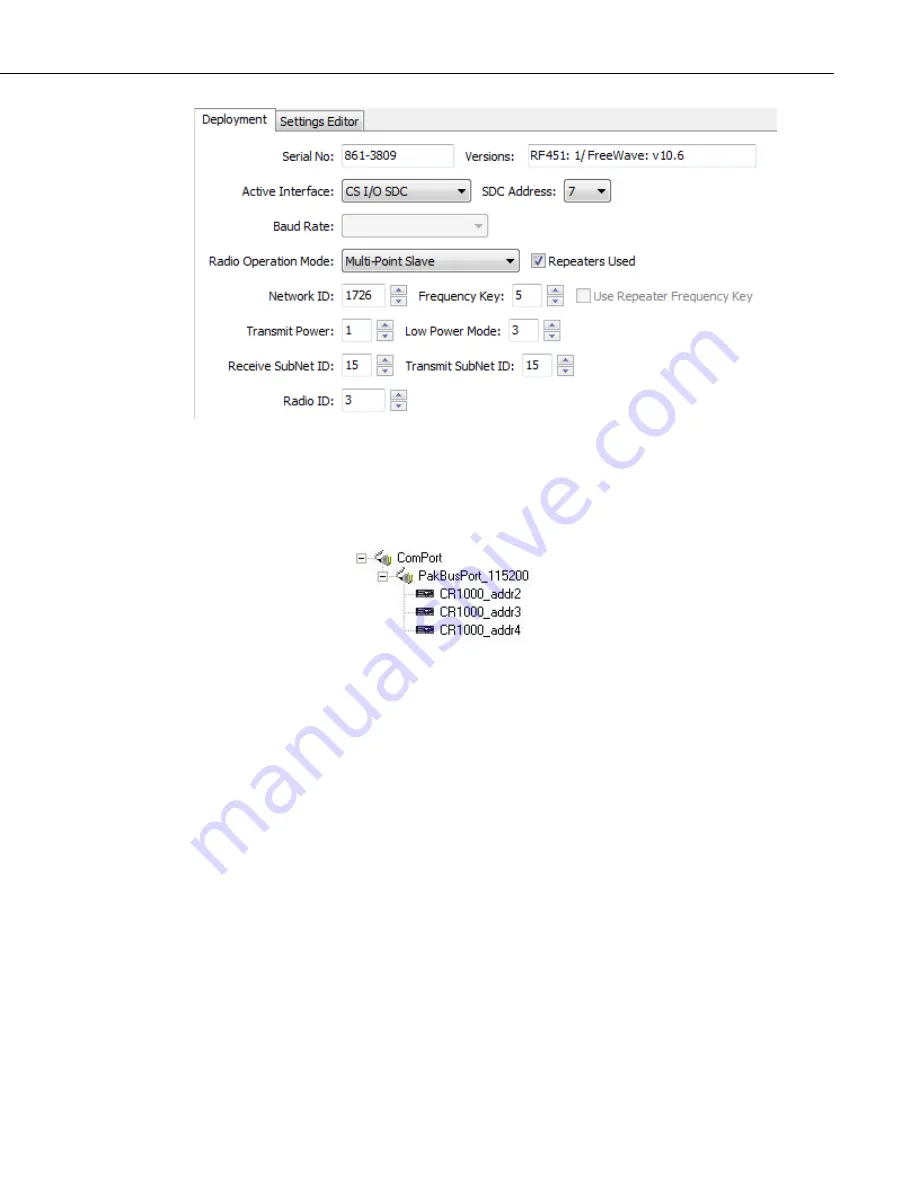
FIGURE B-6. DevConfig Screen Showing Slave Radio Settings for
Example 2
The
Network Map
in the
LoggerNet Setup
screen should look something like
this:
B.3 Example 3: PC-to-RF Network with Parallel
Repeaters (using the SubNet ID)
In this example, the master radio is connected to a PC running
LoggerNet
(see
and TABLE
). One stand-alone repeater (Repeater 1) is used
to access several slave radios connected to CR1000s in the field. The stand-
alone repeater consists of an RF451, power supply, and antenna. Another
repeater (Slave/Repeater) connected to a CR1000 is used to access several
other slave radios on CR1000s.
To take advantage of the low power mode, those devices that are NOT
repeaters should be configured as multi-point slaves and not as multi-point
slave/repeaters. In this configuration, it may be desirable to use an external
omnidirectional antenna at the repeaters.
Note that when a repeater is used, the RF throughput is cut in half. However,
when more than one repeater is used, there is no further degradation in the RF
throughput of the link. Throughput is the rate at which data is sent or received.
Reducing throughput means less data can be transmitted in a specified amount
of time.
Remember, each datalogger must have a unique PakBus address.
Summary of Contents for RF451
Page 2: ......
Page 6: ......
Page 10: ...Table of Contents iv ...
Page 34: ...RF451 Spread Spectrum Radio 24 ...
Page 36: ......
Page 46: ...Appendix B Installation Scenarios B 10 ...
Page 58: ...Appendix D Distance vs Antenna Gain Terrain and Other Factors D 10 ...
Page 60: ......
Page 61: ......