AWS Storage Gateway User Guide
File Gateways
•
•
•
File Gateways
To use a file gateway, you start by downloading a VM image for the file gateway. You then activate the
file gateway from the AWS Management Console or through the Storage Gateway API. You can also
create a file gateway using an Amazon EC2 image.
After the file gateway is activated, you create and configure your file share and associate that share with
your Amazon S3 bucket. Doing this makes the share accessible by clients using either the NFS or SMB
protocol. Files written to a file share become objects in Amazon S3, with the path as the key. There is a
one-to-one mapping between files and objects, and the gateway asynchronously updates the objects in
Amazon S3 as you change the files. Existing objects in the bucket appear as files in the file system, and
the key becomes the path. Objects are encrypted with Amazon S3–server-side encryption keys (SSE-S3).
All data transfer is done through HTTPS.
The service optimizes data transfer between the gateway and AWS using multipart parallel uploads or
byte-range downloads, to better use the available bandwidth. Local cache is maintained to provide low
latency access to the recently accessed data and reduce data egress charges. CloudWatch metrics provide
insight into resource use on the VM and data transfer to and from AWS. CloudTrail tracks all API calls.
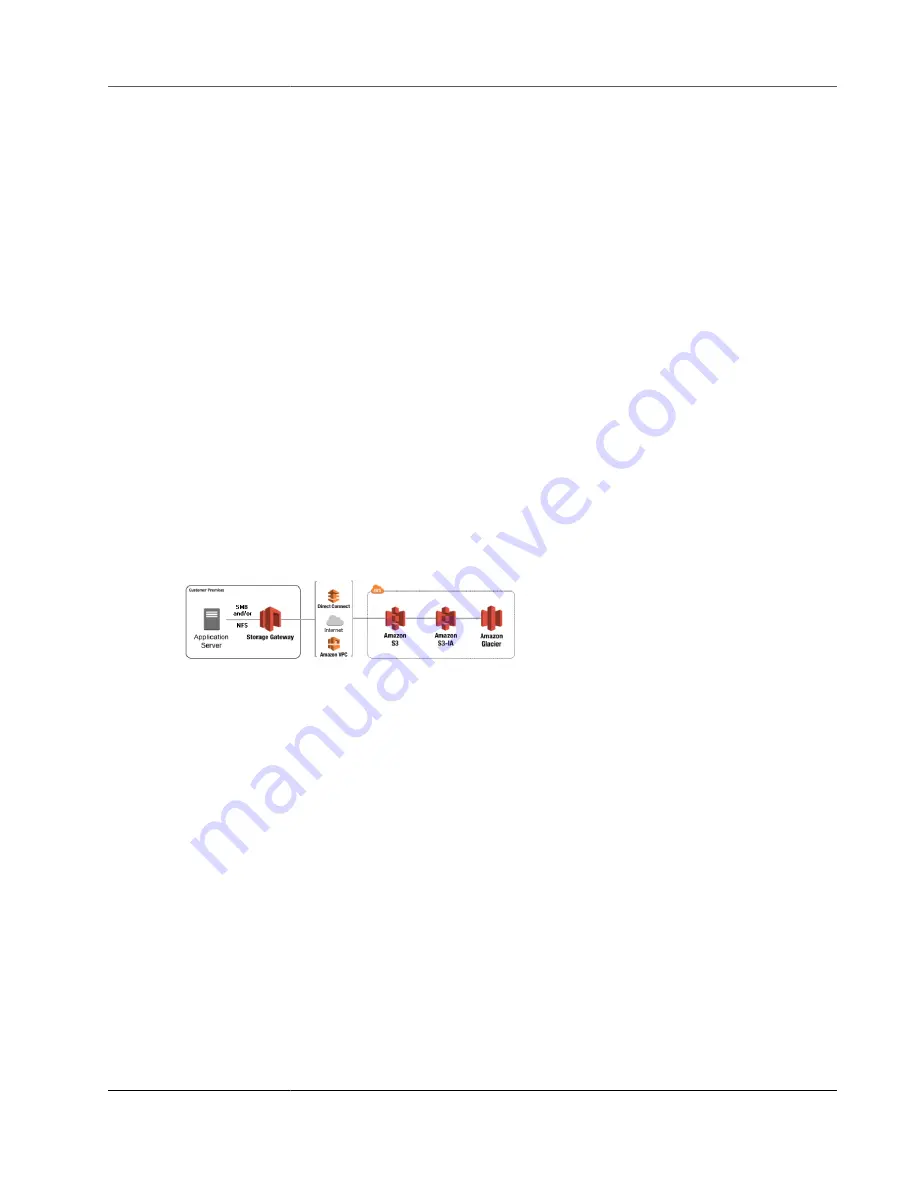
With file gateway storage, you can do such tasks as ingesting cloud workloads to S3, performing backup
and archive, tiering and migrating storage data to the AWS Cloud. The following diagram provides an
overview of file storage deployment for Storage Gateway.
Volume Gateways
For volume gateways, you can use either cached volumes or stored volumes.
Topics
•
Cached Volumes Architecture (p. 3)
•
Stored Volumes Architecture (p. 5)
Cached Volumes Architecture
By using cached volumes, you can use Amazon S3 as your primary data storage, while retaining
frequently accessed data locally in your storage gateway. Cached volumes minimize the need to scale
your on-premises storage infrastructure, while still providing your applications with low-latency access
to their frequently accessed data. You can create storage volumes up to 32 TiB in size and attach to them
as iSCSI devices from your on-premises application servers. Your gateway stores data that you write to
these volumes in Amazon S3 and retains recently read data in your on-premises storage gateway's cache
and upload buffer storage.
Cached volumes can range from 1 GiB to 32 TiB in size and must be rounded to the nearest GiB. Each
gateway configured for cached volumes can support up to 32 volumes for a total maximum storage
volume of 1,024 TiB (1 PiB).
API Version 2013-06-30
3

























