99
ATmega103(L)
0945G–09/01
Memory
Programming
Program and Data
Memory Lock Bits
The ATmega103(L) MCU provides two Lock bits that can be left unprogrammed (“1”) or
can be programmed (“0”) to obtain the additional features listed in Table 35. The Lock
bits can only be erased to “1” with the Chip Erase command.
Note:
1. In Parallel mode, programming of the Fuse bits are also disabled. Program the Fuse
bits before programming the Lock bits.
Fuse Bits
The ATmega103(L) has four Fuse bits, SPIEN, SUT1..0 and EESAVE.
•
When the SPIEN Fuse is programmed (“0”), Serial Program and Data Downloading
is enabled. Default value is programmed (“0”). The SPIEN Fuse is not accessible in
serial programming mode.
•
When EESAVE is programmed, the EEPROM memory is preserved through the
Chip Erase cycle. Default value is unprogrammed (“1”). The EESAVE Fuse bit
cannot be programmed if any of the Lock bits are programmed.
•
SUT1..0 Fuses: Determine the MCU start-up time. See Table 5 on page 26 for
further details. Default value is unprogrammed (“11”), which gives a nominal start-up
time of 16 ms.
The status of the Fuse bits is not affected by Chip Erase.
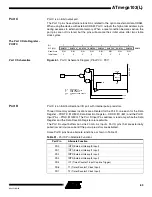
Signature Bytes
All Atmel microcontrollers have a 3-byte signature code that identifies the device. This
code can be read in both serial and parallel mode. The three bytes reside in a separate
address space.
For the ATmega103 they are:
1.
$000: $1E (indicates manufactured by Atmel)
2.
$001: $97 (indicates 128K bytes Flash memory)
3.
$002: $01 (indicates ATmega103 when signature byte $001 is $97)
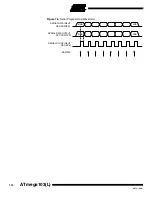
Programming the Flash
and EEPROM
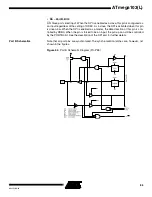
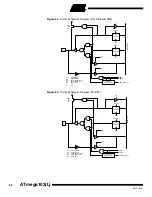
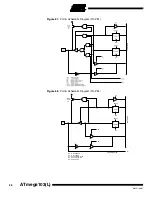
Atmel’s ATmega103(L) offers 128K bytes of In-System reprogrammable Flash memory
and 4K bytes of EEPROM data memory.
The ATmega103(L) is shipped with the On-chip Flash program and EEPROM data
memory arrays in the erased state (i.e., contents = $FF) and ready to be programmed.
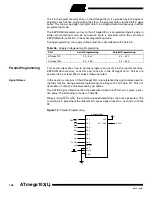
This device supports a parallel programming mode and a serial programming mode.
The +12V supplied to the RESET pin in parallel programming mode is used for program-
ming enable only, and no current of significance is drawn by this pin. The serial
programming mode provides a convenient way to download program and data into the
ATmega103(L) inside the user’s system.
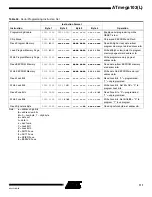
Table 35.
Lock Bit Protection Modes
Memory Lock Bits
Protection Type
Mode
LB1
LB2
1
1
1
No memory lock features enabled.
2
0
1
Further programming of the Flash and EEPROM is disabled.
3
0
0
Same as mode 2, and verify is also disabled.