erensan
°
“
The Heating Engineer
”
06042007
37
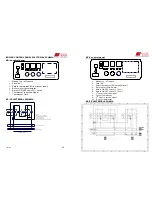
INSTALLATION CIRCUIT DIAGRAM (EXAMPLE)
TR 80 - 350
TR 465-1250
HI
Hydrometer
TS Thermostat 30-90
°
C
TI Thermometer 0-120
°
C
EV
Expansion tank connection sleeve
YS Sanitary hot water connection sleeve
P
Pump
S
Supplying to the system
1.
Supplying to the installation
2.
Returning from the installation
3.
Drain valve
erensan
°
“
The Heating Engineer
”
06042007
38
BOILER FEED WATER AND BOILER WATER CHEMICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
The water to be used in Hot Water boilers should conform to the table values
indicated below.
The boiler feed water and boiler water should be checked constantly and the
chemical conditions required for the water should be ensured in order to
operated the boiler efficiently and economically.
FEEDWATER FOR HOT WATER
BOILERS
Parameter Unit
Make-up water for hot water &
superheated water boilers
bar
total range
Operating Pressure
MPa
total range
Appearance
-
clear, free from suspended solids
Conductivity at 25 °C
µS/cm
< 1500
pH value at 25 °C ¹)
-
> 7,0
Total hardness (Ca + Mg) mgl/liter(ppm)
< 5 [=0,5 Fr.H]
Iron (Fe)
mgl/liter(ppm)
< 0,2
Copper (Cu)
mgl/liter(ppm)
< 0,1
Silica (SiO
2
)
mgl/liter(ppm)
-
Oxygen (O
2
)
mgl/liter(ppm)
-
Oil/grease
mgl/liter(ppm)
< 1
Organic substances
-
See clause 5
1
) With copper alloys in the system the pH value shall be maintained in the range 8,7
to 9,2
2
)
3
)
4) If non-ferrous materials are present in the system, e.g. Aluminium, they may
require lower pH value and conductivity, however, the protection of the boiler has
priority.
5
) If Phosphate is used; considering all other values higher PO4-concentrations are
acceptable, for instance with balanced or coordinated phosphate treatment (see also
clause 4).