Mechatronics
– A combination of mechanical and electrical devices to create a system.
Natural Language
– Language used by humans to communication.
Neural Network
– A network of processing elements that are connected together to simulate the intelli-
gence created by biological brains. Often used to perform pattern recognition.
Open Loop
– in motor control, the lack of a feedback device.
Parallel Data
– Data that is transmitted multiple bits at a time using multiple wires.
Parameters
– Values used to control functions.
Passive Infrared (PIR) sensor
- A type of sensing device that converts infrared energy into electrical
signals. Motion detectors for alarm systems often use PIR sensors to detect moving living objects.
PC/104
– Embedded computer system standard which has connectors with 104 pins. PC/104 modules
are similar to cards found in desktop personal computers except that they stack together instead of plug-
ging into a mother board. Complete computer systems can be created using PC/104 products.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
- A non-conductive board that is laminated with layers of copper to pro-
vide electrical connections between components. ARobot’s controller is a PCB.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
- In motor control, the use of electrical pulses of various widths to
control the motor’s position and speed. In speech and sound creation, the use of various pulse widths to
generate an analog signal by using a low-pass filter.
RAM
– Random Access Memory. Read/write memory.
Remote Control
– Control of a system at a distance.
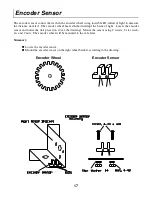
Resolution
– In a motor control system, the smallest motion that a motor can make.
Robot
– Any device that operates automatically performing tasks like a human.
Rule-based System
– See Expert Systems.
Sensor
– A device that converts light, temperature, and other phenomena to electrical signals. Also re-
ferred to as transducer. The ARobot uses many different sensors to detect the environment.
Serial Data
– Data that is transmitted a signal bit at a time over one wire.
Servo Motors RC, DC
– DC (direct current) servo motors use encoder feedback to monitor speed and
position such as ARobot’s drive motor. RC (remote control) servo motors are small servo systems that
include motor, gear train, feedback device, and controller in a small package intended for remote control
airplanes and cars. RC servos are used by ARobot to control the steering.
Software
– Instructions used to direct operations on a CPU.
Sonar
– See Ultrasonic.
Speech Synthesizer
– An electronic device that generates human speech and sounds.
Subsumption Architecture
– A programming method designed by Rodney Brooks of MIT that allows
various functions to subsume other functions based on a predefined priority scheme.
Telepresence
– Control of a robotic system at a different location. The operator may be provided feed-
back using various sensors.
Transistor
– A silicon-based semiconductor device that can be used as an electrical switch or as an am-
plifier.
Ultrasonic
– Sound waves with a frequency greater then humans can detect. Polaroid offers an ultra-
sonic ranging system that can be used to avoid obstacles.
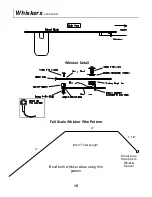
Whiskers
– Hair-like, flexible wires used to detect walls and other objects. ARobot has 2 such whiskers
to aid in navigation.
8
Glossary of Terms
continued
Summary of Contents for ARobot
Page 31: ...About the Controller Board 28 ...
Page 54: ...Robotics com ...