154
Options List
B.11
NTP/PTP Server
B.11.1
General Description
This option provides Network Time Protocol (NTP) and Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
servers in the
Arbiter Model 1201B/C series GNSS clocks. These instructions will assist you in the setup and configuration
of the NTP/PTP server. Configure this option using the Web Interface or the SSH Console.
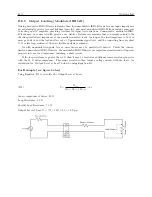
Standard configuration includes two copper Ethernet ports – Option E06. Optionally, order fiber optic
connectors. Standard fiber connector is type LC, 62.5/125 m 50/125 m multimode fiber. Option E07 has
one copper port and one fiber. Option E08 has two fiber ports. Contact the factory for other connector
types.
The NTP/PTP Server has two independent server ports that can access either the NTP (versions 1, 2,
3 or 4 frames) or the PTP servers. This option has been designed in accordance with the latest NTP and
PTP standards and may be updated whenever new firmware is available.
PTP with hardware assist offers much better accuracy than with NTP, however to achieve these accura-
cies requires PTP-enabled network components that provide for latency and jitter to be determined between
the clock and each component. When designing for the ultimate in PTP accuracy, evaluate every component
in the complete network.
Network Time Protocol (NTP) Server
The NTP/PTP Server allows the clock to act as network (NTP) time server over an Ethernet network
and understands NTP version 1 – 4 frames, while optionally supporting authentication via DES and MD5
cryptographic checksums as defined in RFC 5905
. The NTP/PTP Server supports symmetric key authenti-
cation. Time is distributed over the network interface to computers, controllers and other equipment needing
the correct time. The NTP/PTP Server allows a secure connection to configure, using either the preferred
HTTPS Web Interface, or using the SSH Console.
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Server
The NTP/PTP Server allows the clock to act as a Precision Time Server (PTP) according to Standard
IEEE 1588 2008. However for highest accuracy, the entire network where PTP is required must have PTP-
enabled network components. Without hardware assist through the physical interface, PTP will provide
time with the same accuracy as with NTP. Accuracy with hardware assist using PTP should be better than
1 microsecond. Accuracy without hardware assist should be better than 100 microseconds.
Configuration Protocols
Three types of configuration protocols are allowed on the NTP/PTP Server: HTTP, HTTPS and Secure
Shell (SSH). Of the three, HTTPS and SSH permit secure channels on the network between the user and
the NTP/PTP Server. If a secure channel is required, choose either HTTPS using the Web Interface, or
SSH using the Console. HTTPS requires that a valid signed certificate (PEM file) be uploaded into the
NTP/PTP Server. Use of Console does not require a signed certificate. Both of these methods are discussed
in the following pages, and both require a Username and Password to open a connection. To access the
option configuration use the Web Interface you will need Web browser. To access the NTP/PTP Server
using the Console, you will need an SSH client. These instructions use an SSH client called PuTTY when
describing the Console Interface. NTP/PTP Server comes by default configured for an HTTP connection,
and may be configured to use HTTPS.
2
IEEE 1588v2 – IEEE 1588-2008
3
Includes RFC 5906, 5907 and 5908
Summary of Contents for 1201B
Page 4: ...iv ...
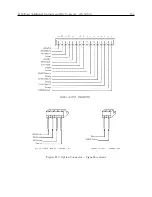
Page 153: ...B 7 Four Fiber Optic Outputs 135 Figure B 4 Jumper Locations ...