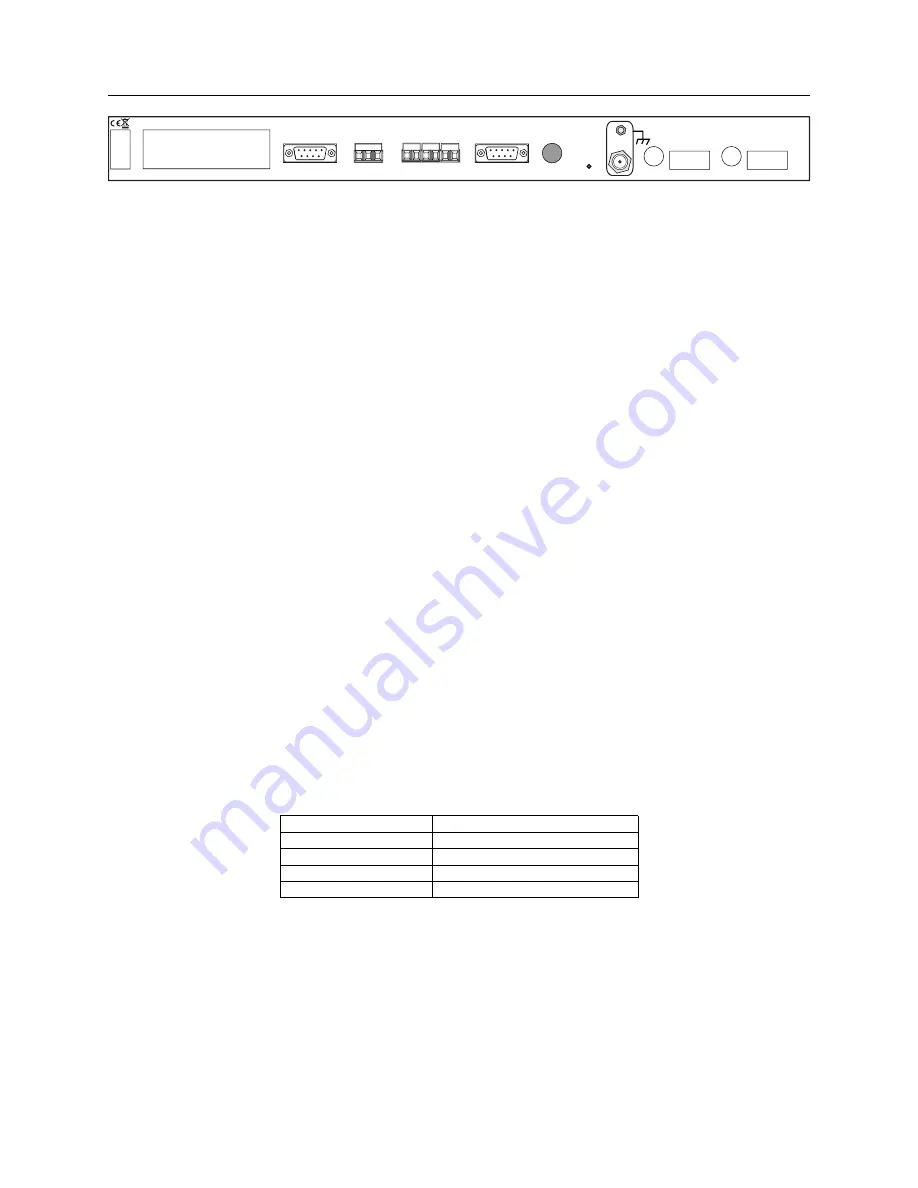
9.2 Timing Output Description
75
B1234
Arb
it
e
r Sy
st
e
m
s
Serial Number
Made in USA
ANTENNA
FIBER
COM1
RELAY
COM2
INTERNAL OPTION SPACE
POWER B
POWER A
1
I/O PORTS
2
3
ANTENNA
STATUS
Figure 9.1: Rear Panel Descriptions, optional outputs may be shown
9.2.1
Inputs and Outputs: Port 1, Port 2, Port 3
Three, Phoenix-style, terminal connectors supply timing signals to external equipment and may
also be configured for an event input. All three standard ports can source unmodulated IRIG-B, 1
PPS (pulse per second), and Programmable Pulse. Port 2 may also source modulated IRIG-B.
9.2.2
Digital Drivers
Each of the digital outputs is driven by a CMOS 74HCxxx quad driver capable of supplying 75
mA at 5 Vdc. Each I/O port may distribute timing signals to a number of devices depending on
the total load current drawn by all of the connected devices. To determine the number of devices
you can supply from each output, calculate the load current required by each connected device.
For example, if the IED timing signal input (e.g. IRIG-B003) requires 10 mA, one digital output
should be able to support up to eight identical devices.
9.2.3
Analog Driver
Modulated IRIG-B is available at Port 2 and uses an analog driver exclusively for this purpose.
Using an AD8531 amplifier, the analog driver supplies 4.5 volts peak-to-peak (Vpp) to a 20 Ω
source resistor, then to the output connector. The modulated IRIG-B output should provide a
minimum of 3 Vpp with a connected load of 50 Ω.
As the load current increases (by adding external loads), more voltage is dropped across the
clock source resistor causing the drive voltage to decrease. To assure detection by your equipment,
make sure to match the modulated output to within the required voltage range of the receiving
equipment.
Table 9.1 shows how the actual drive voltage varies with increasing load current.
Matching the analog output to your devices should be easy, however in some cases it may be
necessary to match the available drive voltage to the IED through use of a dropping resistor.
Drive Current, mA
Actual Drive Voltage, Vpp
0
4.5
1
4.48
10
4.3
100
2.5
Table 9.1: Drive Current vs. Voltage
















































