UG-600
Evaluation Board User Guide
Figure 3. Register Control for the
GUI Page 1
Figure 4. Register Control for the
GUI Page 2
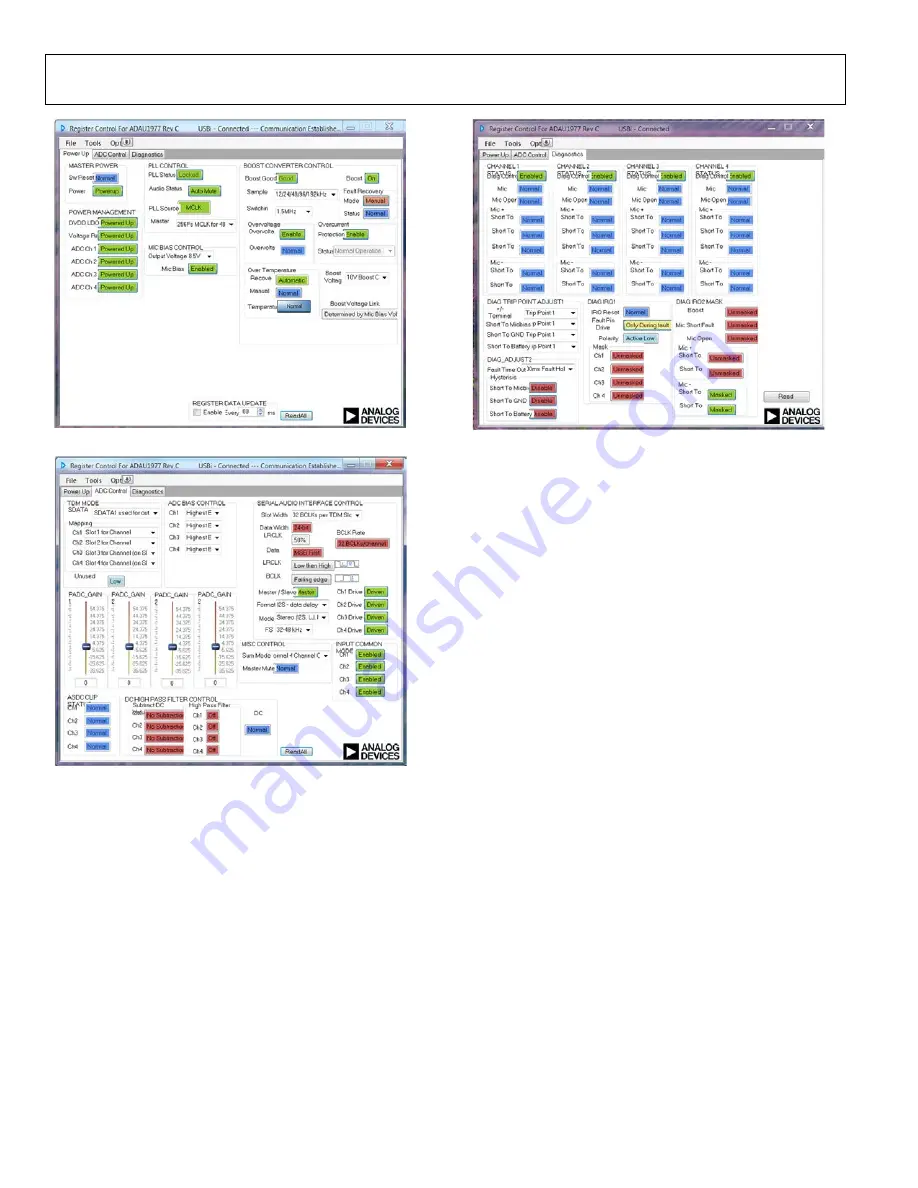
Figure 5. Register Control for the
GUI Page 3
MICROPHONE DIAGNOSTICS
Microphone diagnostics are applicable for the
only,
used with the microphone input application circuit, as
described in the
data sheet.
1.
Connect the microphone to the desired input connector:
J17, J28, J38, or J47.
2.
Ensure that the inputs are dc-coupled by setting Switches
S10, S16, S21, and S26 to
On
.
3.
Select the appropriate bias resistors using Switches S7 and
S12 for Channel 1, Switches S15 and S18 for Channel 2,
Switches S20 and S23 for Channel 3, Switches S25 and S29
for Channel 4. The resistor options are 300 Ω or 500 Ω.
4.
Select the internal microphone bias by setting Jumpers J22,
J31, J41, J51 to the
INT
position.
5.
Ensure that the
Boost Good
indicator is green on the GUI
Power Up
tab.
6.
Ensure
Boost
is
On
.
7.
By default, the 48 k sample rate is selected, and the boost
switching frequency is 1.5 MHz.
8.
In the
MIC BIAS CONTROL
section, select the desired
microphone bias output voltage (see Figure 3). By default,
it is 8.5 V.
9.
Ensure
Mic Bias
is
Enabled
(see Figure 3).
10.
Check the microphone bias voltage output on the
11.
Go to the
Diagnostics
tab on the GUI (see Figure 5).
12.
With the microphone connected, the typical voltage at the
positive (+) input is 2/3 of microphone bias, and at the
negative (−) input is 1/3 of microphone bias.
13.
Click
Read
in the
Diagnostics
tab on the GUI (see Figure 5).
14.
With proper connections and normal working conditions,
all of the channel status indicators will be blue for each
respective channel connected with the microphone.
15.
To check the diagnostics functionality, create a fault situation
at the microphone input. This fault situation is done by
1
1751-
003
1
1751-
004
1
1751-
005
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 27























