507868-01
Page 20 of 48
Issue 1912
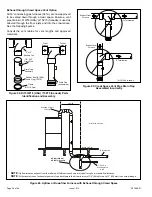
Follow the next two steps when installing the unit in Non-
Direct Vent applications where combustion air is taken
from indoors and flue gases are discharged outdoors.
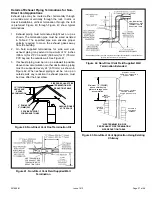
1. Use field-provided materials and the factory-provided
air intake screen to route the intake piping as shown
in Figure 29. Maintain a minimum clearance of 3” (76
mm) around the air intake opening. The air intake
opening (with the protective screen) should always be
directed forward, or sideways.
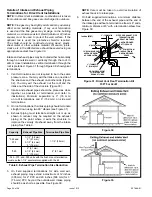
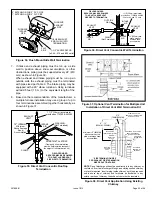
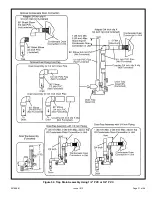
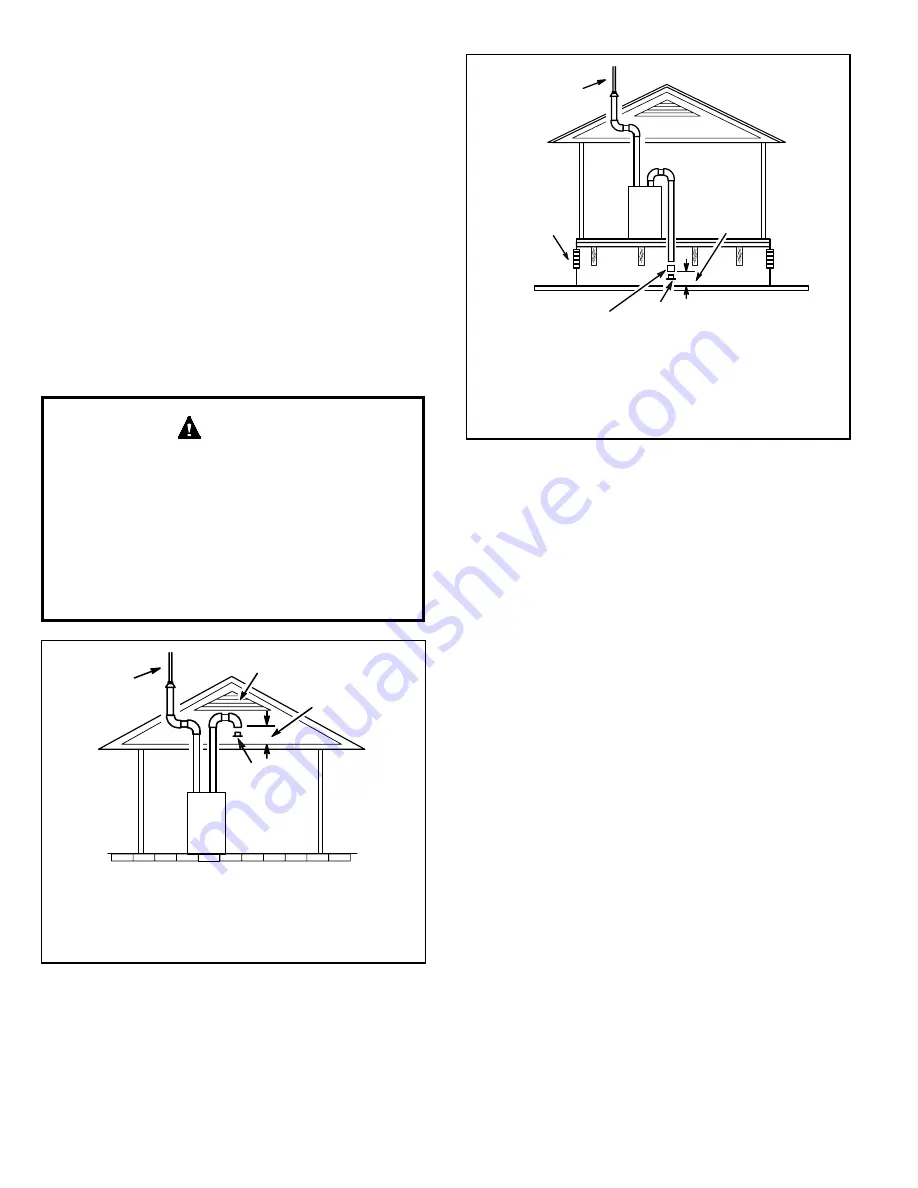
2. If intake air is drawn from a ventilated attic (Figure
26) or ventilated crawlspace (Figure 27) the exhaust
vent length must not exceed those listed in Table 7B.
If 3” diameter pipe is used, reduce to 2” diameter pipe
at the termination point to accommodate the debris
screen.
3. Use a sheet metal screw to secure the intake pipe to
the connector, if desired.
If this unit is being installed in an application with
combustion air coming in from a space serviced by an
exhaust fan, power exhaust fan, or other device which
may create a negative pressure in the space, take care
when sizing the inlet air opening. The inlet air opening
must be sized to accommodate the maximum volume
of exhausted air as well as the maximum volume of
combustion air required for all gas appliances serviced
by this space.
CAUTION
Ventilation Louvers
Inlet Air
(Minimum 12 in.
(305mm) above
Attic Floor)
Roof Terminated
Exhaust Pipe
Furnace
*Intake Debris
Screen
(Provided)
* See Maximum Vent Lengths table
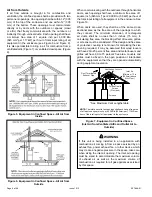
NOTE:
The inlet and outlet air openings shall each have a free area
of at least one square inch per 4,000 Btu (645mm
2
per 1.17kW) per
hour of the total input of all equipment in the enclosure.
Figure 26.
Equipment in Confined Space
(Inlet Air from Ventilated Attic and Outlet Air to
Outside)
Roof Terminated
Exhaust Pipe
Furnace
Ventilation
Louvers
(Crawl Space)
*Intake Debris Screen Provided
Inlet Air
Minimum
12 in. (305mm)
above Crawl
Space Floor
Coupling or
3 in. to 2 in.
Transition
(Field Provided)
* See Maximum Vent Lengths table
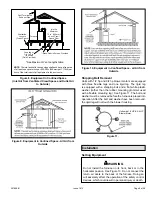
NOTE:
The inlet and outlet air openings shall each have a free area
of at least one square inch per 4,000 Btu (645mm
2
per 1.17kW) per
hour of the total input of all equipment in the enclosure.
Figure 27.
Equipment in Confined Space
(Inlet Air from Ventilated Crawl Space and Outlet Air
to Outside)
General Guidelines for Vent Terminations
In Non-Direct Vent applications, combustion air is taken
from indoors and the flue gases are discharged to the
outdoors. This unit is then classified as a non-direct vent,
Category IV gas furnace.
In Direct Vent applications, combustion air is taken from
outdoors and the flue gases are discharged to the outdoors.
This unit is then classified as a direct vent, Category IV gas
furnace.
In both Non-Direct Vent and Direct Vent applications, the
vent termination is limited by local building codes. In the
absence of local codes, refer to the current National Fuel
Gas Code ANSI Z223-1/NFPA 54 in U.S.A., and current
CSA-B149 Natural Gas and Propane Installation Codes in
Canada for details.
Position termination according to location given in Figure
29 or Figure 30. In addition, position termination so it is
free from any obstructions and 12” above the average
snow accumulation.
At vent termination, care must be taken to maintain
protective coatings over building materials (prolonged
exposure to exhaust condensate can destroy protective
coatings). It is recommended that the exhaust outlet not be
located within 6 feet (1.8 m) of a condensing unit because
the condensate can damage the painted coating.
NOTE:
See Table 8 for maximum allowed exhaust pipe
length without insulation in unconditioned space during
winter design temperatures below 32°F (0°C). If required