3
Alcatel-Lucent | ENUM Use and Management for the Successful Deployment of ENUM-Enabled Services
Overview of ENUM in IMS
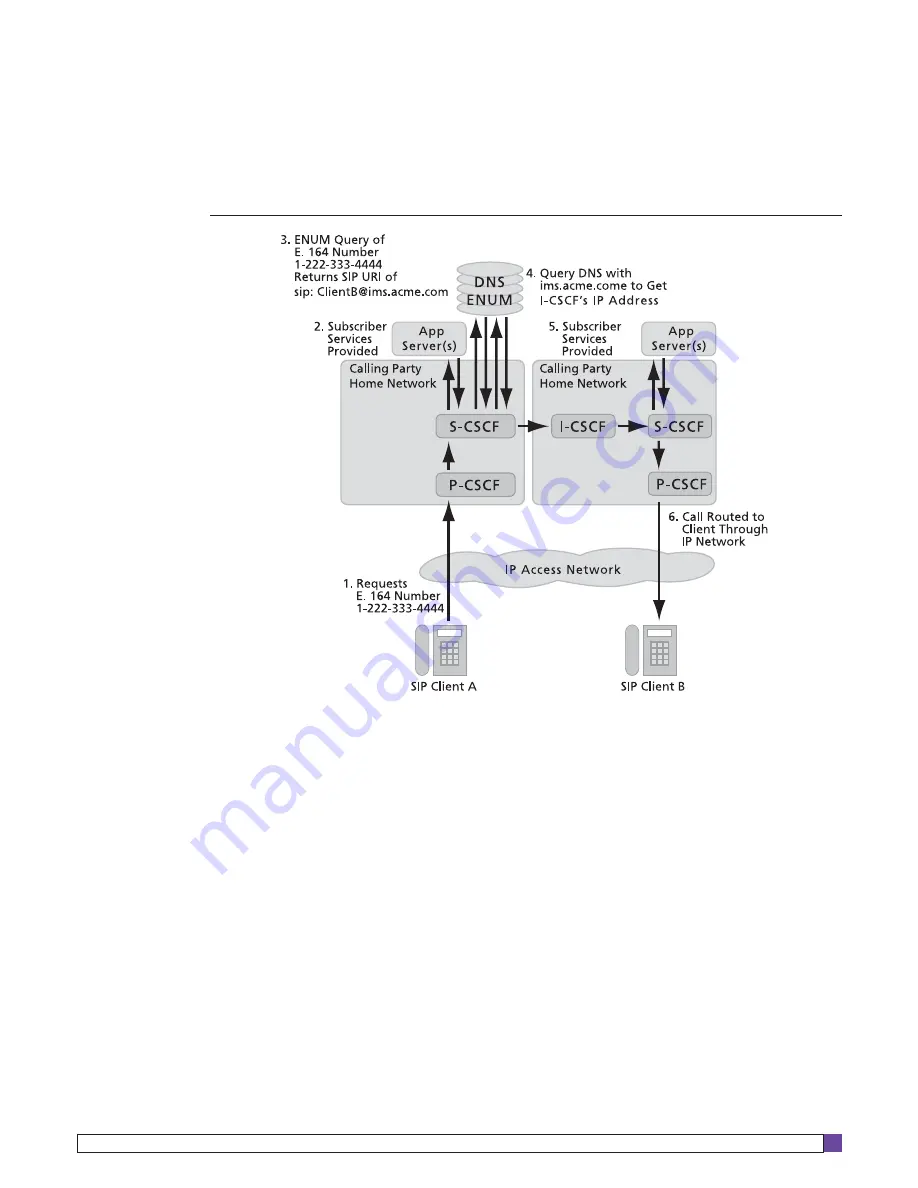
Below are summaries for two example call flows for VoIP calls made using an IMS network that
uses ENUM. In the first scenario, which is depicted in the figure below, one IMS subscriber calls
another IMS subscriber.
In this case, the following steps are carried out to setup and route the call through the IP network.
1. User of SIP Client A calls E.164 number of
1-222-333-4444
in order to reach user of SIP Client B.
2. The Serving - Call Session Control Function (S-CSCF) communicates with the Application Server to
provide subscriber services.
3. The S-CSCF queries the DNS/ENUM server with the E.164 number, and it returns the SIP URI of
sip:[email protected].
4. The S-CSCF queries the DNS/ENUM server again to get the host IP address for ims.acme.com. This IP
address is the address of the Interrogating-CSCF (I-CSCF). (Note that in most networks the DNS and
ENUM servers are usually separate servers, but are illustrated above as a single server for simplification.
Also, although not shown, the following is done: the S-CSCF sends a SIP Invite message to the I-CSCF,
and it querries the Home Subscriber Server [not shown] in the Called Party Home Network to determine
the S-CSCF currently serving Client B.)
5. The S-CSCF in the Called Party Home Network communicates with the Application Server to
provide subscriber services.
6. A sesion is established between the two endpoints, and bearer traffic between them is routed through
the IP access and backbone networks.
Figure 2: IMS Subscriber-to-IMS Subscriber Call












