2.12 Ventilation
01-999021-00 A0100
Installation Planning Guide
21
2.12 Ventilation
Air ventilation must be adequate to displace
the liquid helium gas during a quench,
especially when using any type of volatile
liquid for variable temperature experiments.
Consult with a safety engineer on this
subject. Gaseous helium or nitrogen
exhausted from the magnet will displace
oxygen and cause asphyxiation if not
properly ventilated. During a magnet quench,
the evaporated helium is exhausted from the
manifold by the pressure relief valves. The
amount of gas depends on the amount of
liquid helium held by the magnet.
lists the amount of liquid helium for each
magnet.
The expansion ratio of liquid helium at room
temperature is about 740:1, meaning that for
every liter of liquid helium you get about 740
liters of helium gas
2.13 Helium and Nitrogen Refill Volumes and Intervals
lists typical refill volumes and intervals for helium and nitrogen. Locating a
reliable local source of liquid helium and nitrogen is particularly important. Use the values
listed in
when making arrangements for an on-going supply of liquid helium and
liquid nitrogen.
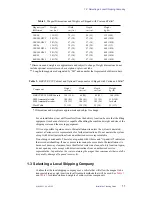
Table 9. Liquid Helium Displacement
for Room Ventilation Considerations
Magnet/Bore
(MHz/mm)
LHe Max. Volume
(liters)
200/54
30
200/54 LH235
87
200/54 LH365
136
300/54
30
300/54 LH235
87
300/54 LH365
136
400/54
74
400/54 LH365
123
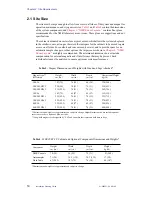
Table 10. Helium and Nitrogen Refill Intervals and Volumes
Magnet
(MHz/mm)
Helium Refill Interval
(Days)
Helium Refill Volume
(Liters)
Nitrogen Refill Interval
(Days)
Nitrogen Refill Volume
(Liters)
200/54
80
26
14
32
200/54 LH235
235
79
14
61
200/54 LH365
365
122
14
67
300/54
80
26
14
32
300/54 LH234
234
78
14
61
300.54 LH365
365
122
14
67
400/54
183
61
14
61
400/54 LH365
365
106
14
67