28 Getting Started
Chapter 1
Card Numbers
The card number (cc of the channel_list) identifies the module within a
switchbox. The card number assigned depends on the switch configuration
used. Leading zeroes can be ignored for the card number.
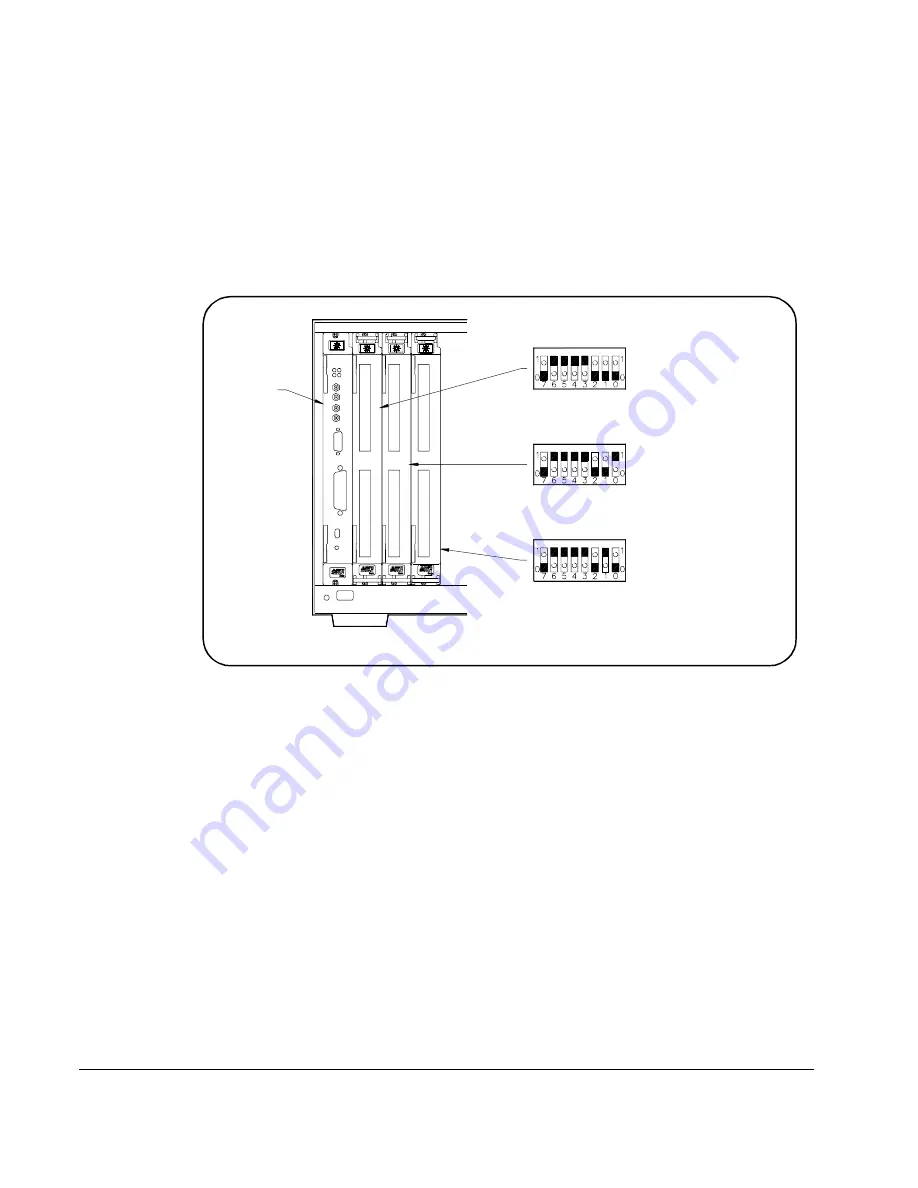
In a single-module switchbox configuration, the card number is always 01.
In a multiple-module switchbox
configuration, modules are set to successive
logical addresses.
The module with the lowest logical address is always card number 01. The
module with the next successive logical address is card number 02, etc.
Figure 1-15 illustrates card numbers and logical addresses of a typical
multiple-module switchbox configuration.
Channel Addresses
The channel address (nn of the channel list) determines which relay on the
selected card will be addressed. Form C switch channel numbers are 00
through 31. The channels can be addressed using channel numbers or
channel ranges:
•
single channels (@ccnn);
•
multiple channels (@ccnn,ccnn,...);
•
sequential channels (@ccnn:ccnn);
•
groups of sequential channels (@ccnn:ccnn,ccnn:ccnn);
•
or any combination of the above.
Use a comma (,) to form a channel list or a colon (:) to form a channel range.
Only valid channels can be accessed in a channel list or channel range.
Also, the channel range must be from a lower channel number to a higher
channel number. For example,
CLOS(@100:215)
is acceptable, but
CLOS(@215:100)
generates an error.
Figure 1-15. Typical Card Numbers in a Multiple-module Switchbox
Command
Module
Note: Physical placement of the Module in the Logical Address
order is not required, but is recommended.
Switch Module
Logical Address = 120
Secondary Address = 15
Card Number 01
Logical Address = 121
Switch Module
Switch Module
Logical Address = 122
1
2
8
6
4
3
2
1
6
8
4
2
1
Card Number 02
6
4
1
2
8
1
6
3
2
8
4
1
2
Card Number 03
6
4
1
2
8
1
6
3
2
8
4
1
2
Summary of Contents for E1463A
Page 2: ......
Page 6: ...6 Notes ...
Page 10: ...10 Notes ...
Page 78: ...78 Form C Switch Specifications Appendix A Notes ...
Page 98: ...98 Index Notes ...
















































