GUID-50908C66-1C3B-4D1F-A7FC-B9429ACC9120 V1 EN
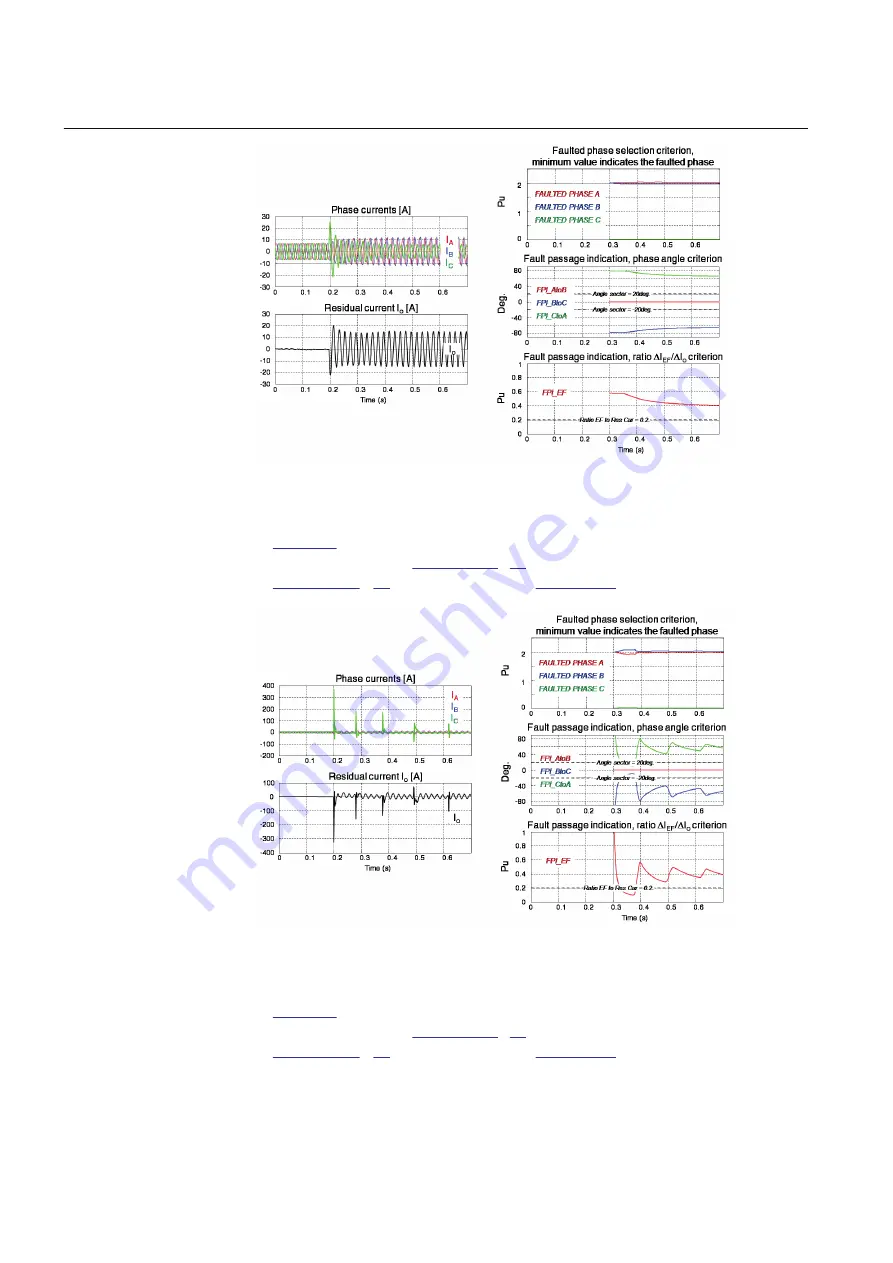
Figure 85:
Stable phase C-to-earth fault current flowing through the measuring
point of FPIPTOC in a compensated network
In
, the fault occurs at time 0.2 sec. On the right-hand side, the result of
faulted phase selection (
) and fault passage indication (phase angles
of
EF
/ΔI
o
ratio of
GUID-D67DCE74-A2C9-457D-B0B8-9139214C1C75 V1 EN
Figure 86:
Re-striking phase C-to-earth fault current flowing through the
measuring point of FPIPTOC in a compensated network
In
, the fault occurs at time 0.2 sec. On the right-hand side, the result of
faulted phase selection (
) and fault passage indication (phase angles
of
EF
/ΔI
o
ratio of
Section 6
1MRS757488 H
Commissioning
156
RIO600
Installation and Commissioning Manual
Summary of Contents for Remote I/O RIO600
Page 1: ... Remote I O RIO600 Installation and Commissioning Manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 8: ......
Page 14: ...6 ...
Page 18: ...10 ...
Page 64: ...56 ...
Page 280: ...272 ...
Page 306: ...298 ...
Page 310: ...302 ...
Page 311: ...303 ...
















































