en06000607_ansi.vsd
~
21
X
S
X
L1
I
F
v
V
M
Source
Fault voltage
Pre -fault voltage
X
C
Source voltage
V’
M
With bypassed
capacitor
With inserted
capacitor
F
X
ANSI06000607 V1 EN-US
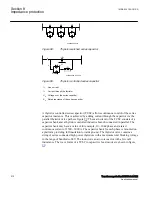
Figure 94:
Current inversion on series compensated line
The relative phase position of fault current I
F
compared to the source voltage V
S
depends in general on the character of the resultant reactance between the source and
the fault position. Two possibilities appear:
1
1
0
0
-
+
>
-
+
<
S
C
L
S
C
L
X
X
X
X
X
X
EQUATION1935 V1 EN-US
(Equation 59)
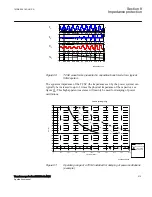
The first case corresponds also to conditions on non compensated lines and in cases,
when the capacitor is bypassed either by spark gap or by the bypass switch, as shown
in phasor diagram in figure
. The resultant reactance is in this case of inductive
nature and the fault currents lags source voltage by 90 electrical degrees.
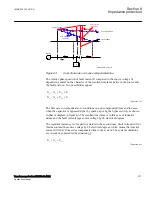
The resultant reactance is of capacitive nature in the second case. Fault current will for
this reason lead the source voltage by 90 electrical degrees, which means that reactive
current will flow from series compensated line to the system. The system conditions
are in such case presented by equation
1
>
+
C
S
L
X
X
X
EQUATION1936 V1 EN-US
(Equation 60)
1MRK 504 163-UUS A
Section 8
Impedance protection
Transformer protection RET670 2.2 ANSI
217
Application manual
Summary of Contents for RELION RET670
Page 1: ...RELION 670 SERIES Transformer protection RET670 Version 2 2 ANSI Application manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 48: ...42 ...
Page 64: ...58 ...
Page 74: ...68 ...
Page 104: ...98 ...
Page 194: ...188 ...
Page 518: ...512 ...
Page 618: ...612 ...
Page 648: ...642 ...
Page 666: ...660 ...
Page 672: ...666 ...
Page 682: ...676 ...
Page 844: ...838 ...
Page 868: ...862 ...
Page 956: ...950 ...
Page 964: ...958 ...
Page 1004: ...998 ...
Page 1014: ...1008 ...
Page 1015: ...1009 ...