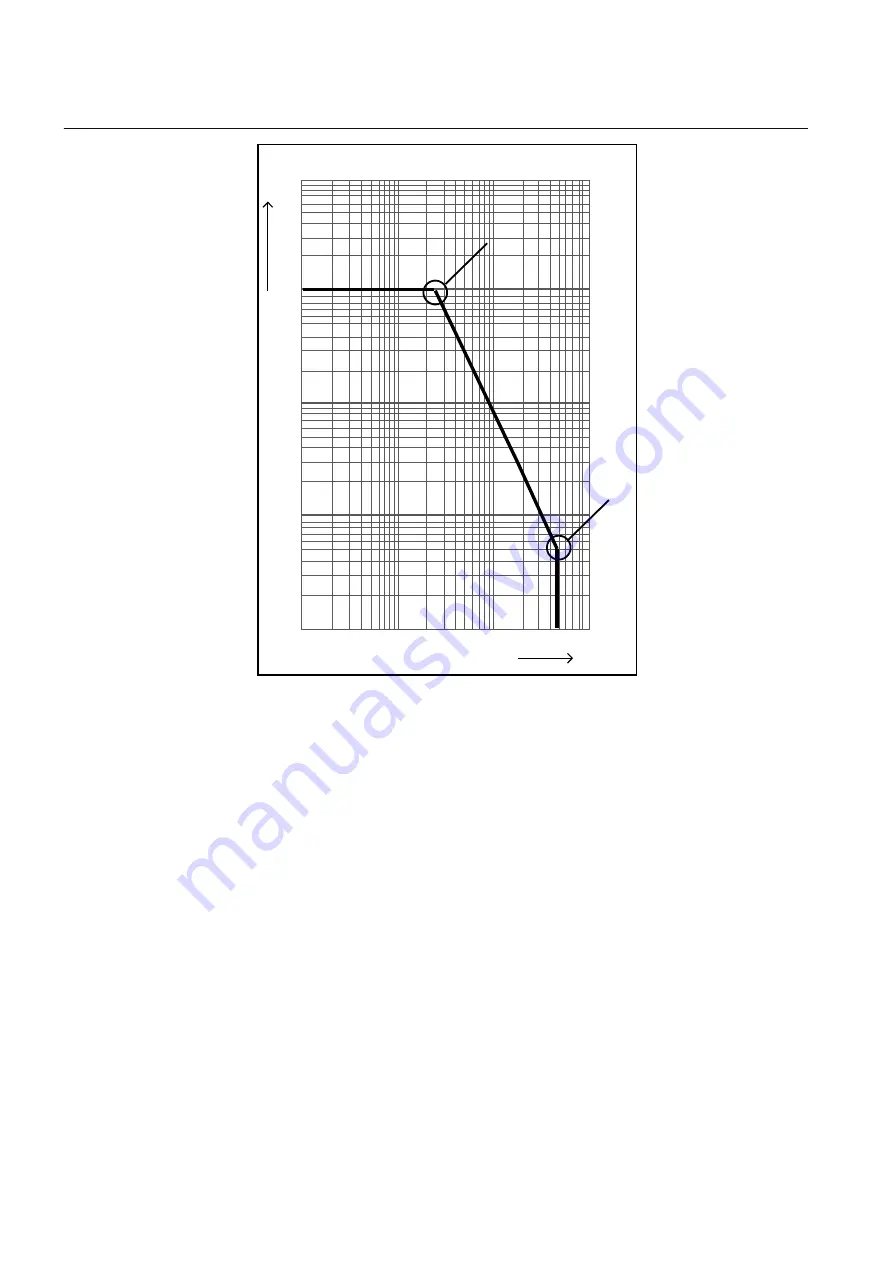
N
u
m
b
e
r
o
f
m
a
ke
-b
re
a
k
op
e
ra
tio
n
s
(
n
)
Interrupted current (kA)
P1
P2
100000
50000
20000
10000
2000
5000
1000
100
200
500
10
20
50
0.1
0.2
0.5
1
2
5
10
20
50
100
IEC12000623_1_en.vsd
IEC12000623 V1 EN-US
Figure 162:
An example for estimating the remaining life of a circuit breaker
Calculation for estimating the remaining life
The graph shows that there are 10000 possible operations at the rated operating
current and 900 operations at 10 kA and 50 operations at rated fault current.
Therefore, if the interrupted current is 10 kA, one operation is equivalent to
10000/900 = 11 operations at the rated current. It is assumed that prior to tripping,
the remaining life of a breaker is 10000 operations. Remaining life calculation for
three different interrupted current conditions is explained below.
•
Breaker interrupts at and below the rated operating current, that is, 2 kA, the
remaining life of the CB is decreased by 1 operation and therefore, 9999
operations remaining at the rated operating current.
•
Breaker interrupts between rated operating current and rated fault current, that
is, 10 kA, one operation at 10kA is equivalent to 10000/900 = 11 operations at
the rated current. The remaining life of the CB would be (10000 – 10) = 9989
at the rated operating current after one operation at 10 kA.
•
Breaker interrupts at and above rated fault current, that is, 50 kA, one
operation at 50 kA is equivalent to 10000/50 = 200 operations at the rated
Section 15
1MRK 506 375-UEN A
Monitoring
392
Railway application RER670 2.2 IEC
Application manual
Summary of Contents for RELION RER670
Page 1: ...RELION 670 SERIES Railway application RER670 Version 2 2 IEC Application manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 22: ...16 ...
Page 48: ...42 ...
Page 70: ...64 ...
Page 80: ...74 ...
Page 100: ...94 ...
Page 210: ...204 ...
Page 364: ...358 ...
Page 384: ...378 ...
Page 468: ...462 ...
Page 494: ...488 ...
Page 504: ...498 ...
Page 505: ...499 ...
















































