Power Break® II Devices
Draw-Out Device Installation
Description
Types SSD and SHD Power Break II draw-out circuit breakers
are used in types SPS and SPH substructures, with
appropriate catalog numbers listed in Table 1. Power Break II
switches are used only with type SP
S
substructures, with
appropriate catalog numbers listed in Table 2. Draw-out
construction permits activation of a new feeder, allows rapid
replacement of a device, and facilitates inspection and
maintenance of the draw-out device with no need to de-
energize the entire switchboard.
Draw-Out Breaker
Substructure
SSD08X2##
SPSDOS08
SHD08X2##
SPHDOS08
SSD16X2##
SPSDOS16
SHD16X2##
SPHDOS16
SSD20X220
SPSDOS20
SHD20X220
SPHDOS20
SSD25X###
SPSDOS25
SHD25X###
SPHDOS25
SSD30X3##
SPSDOS30
SHD30X3##
SPHDOS30
SSD40X4##
SPSDOS40
SHD40X4##
SPHDOS40
Note: In the circuit breaker catalog number, replace “X” with "G" for
EntelliGuard
®
Trip
U
nit
s
or
“B” for MicroVersaTrip Plus™ or
MicroVersaTrip PM™ Trip Units or with “D” for Power+™ Trip Units
—
Table 1. Catalog numbers of draw-out circuit breakers and corresponding substructures.
Draw-Out Switch
Substructure
S
S
D08
X
2##
SP
S
DOS08
S
S
D16
X
2##
SP
S
DOS16
S
S
D20
X
2##
SP
S
DOS20
S
S
D25
X
###
SP
S
DOS25
S
S
D30
X
3##
SP
S
DOS30
S
S
D40
X
4##
SP
S
DOS40
Features
The features described below are illustrated in Figures 1, 2,
and 3.
Primary Disconnects.
Primary power is fed through multiple-
finger primary disconnects when the device is in the
connected position.
Secondary Disconnects.
Control power is provided through
the secondary disconnects in the test and connected
positions only. All accessories terminate at dedicated
positions regardless of the combination of accessories
installed.
Rollers. The rollers on the sides of the device ride on retract-
able rails in the draw-out substructure for easy installation
and removal.
Draw-Out Mechanism. A racking shaft powers a centrally
mounted screw through a chain drive into a fixed nut in the
substructure. A special speed wrench is supplied with an
integral
1
/
2
-inch square-drive socket to aid in installation
and removal.
Racking Shaft Wrench Lockout Plate. This interlock prevents
engagement of the wrench when the device contacts are
closed.
—
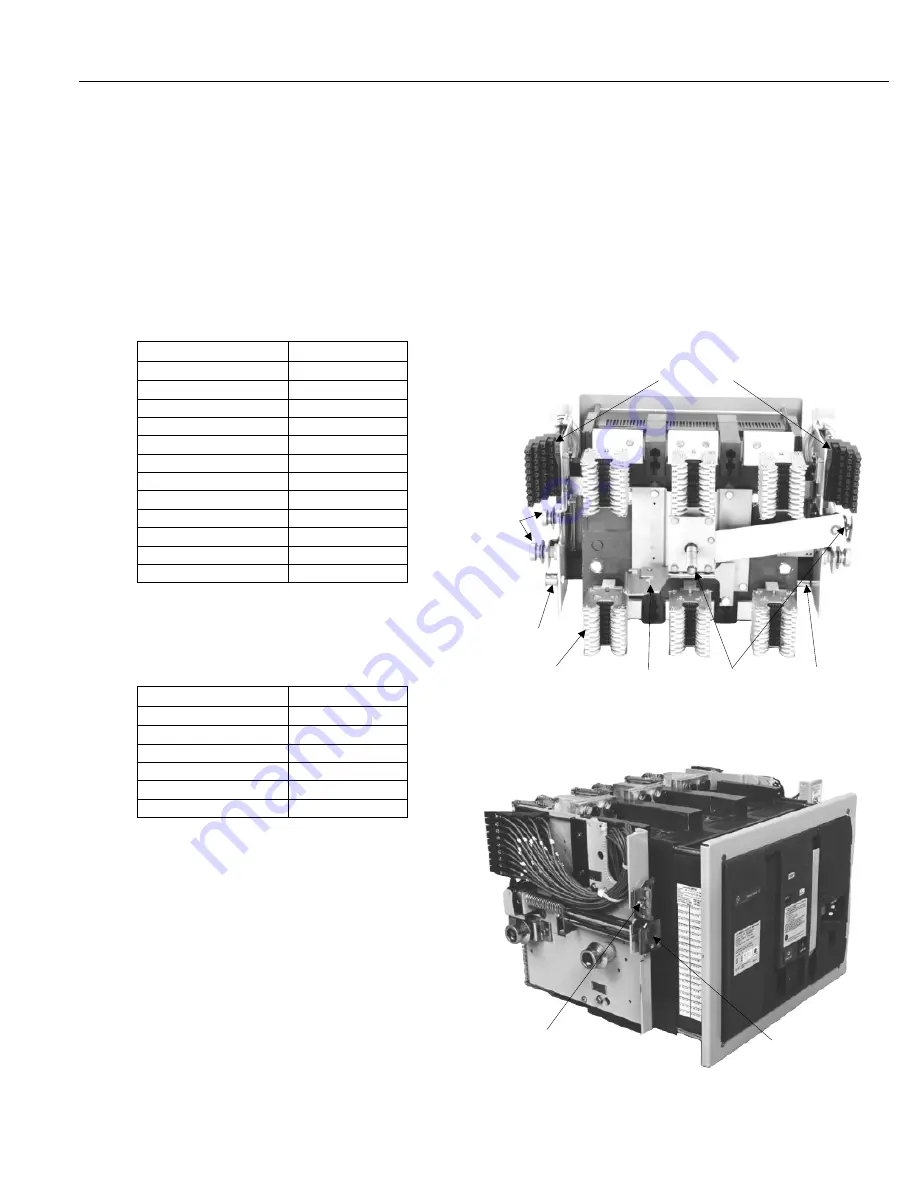
Figure 1. Rear view of the Power Break® II draw-out device.
Shutter
Actuator
Primary
Disconnects
Draw-Out
Interlock
Draw-Out
Mechanism
Bypass Switch
Actuator
Secondary
Disconnects
Rollers
Draw-Out
Padlock
Accessory
Cat. No. TDOPC
Racking Shaft
Wrench Lockout
Plate
—
Table 2. Catalog numbers of draw-out switches and corresponding substructures.
—
Figure 2. Left side of the device, showing the padlock accessory and racking shaft lockout plate.
1
Note: In the switch catalog number, replace “X” with "W"
for
EntelliGuard ®
Control
U
nit
s
or with
“
Y
” for Power+™
Control
Unit
s






















