3Com Router Module Guide
Chapter 3 Multifunctional Interface Modules
3-47
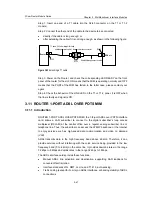
Step 1: Insert one end of a T1 cable into the RJ-45 connector on the T1 or T1-F
module;
Step 2: Connect the other end of the cable to the device to be connected:
z
directly if the cable is long enough; or
z
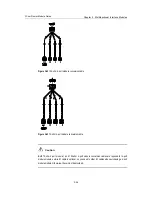
after extending the cable if it is not long enough, as shown in the following figure:
Router
DDN, etc
RJ45
Network interface connector
RJ45
Straight-through network cable
RJ45
shielding network cable)
T1 cable (100-ohm straight-through
Figure 3-52
Extending a T1 cable
Step 3: Power on the Router, and check the corresponding LED READY on the front
panel of the router for the slot: ON means that the MIM is operating normally and OFF
means that the POST of the MIM has failed. In the latter case, please contact your
agent;
Step 4: Check the behavior of the LINK LED on the T1 or T1-F panel. It is OFF when
the line is faulty and signal is Off.
3.11 ROUTER 1-PORT ADSL OVER POTS MIM
3.11.1 Introduction
ROUTER 1-PORT ADSL OVER POTS MIM/, the 1-/2-port ADSL over PSTN interface
card, allows a LAN subscriber to connect to the digital subscriber's loop access
multiplexer (DSLAM) at the central office over a regular analog subscriber line or
telephone line. Thus, the subscriber can access the ATM/IP backbone or the Internet
to enjoy services such as high-speed data communication and video on demand
(VoD).
ADSL transmits data in the high frequency band above 26 kHz. Therefore, it can
provide services without interfering with the voice service being provided in the low
frequency band (0 to 4 kHz) on the same line. It provides downlink rates in the range
32 kbps to 8 Mbps and uplink rates in the range 32 kbps to 1 Mbps.
The ADSL interface cards provide these functions:
z
Manual ADSL line activation and deactivation, supporting SAR loopback for
convenient fault isolation.
z
Interface standards of G. DMT, G. Lite, and T1.413, auto-sensing.
z
Trellis coding (except for G. Lite) on ADSL interfaces, enhancing stability of ADSL
connections.