5.2 Motor Stopping Methods for Servo OFF and Alarms
5-3
5
Basic Functions That Requir
e Setting befor
e Operation
5.2
Motor Stopping Methods for Servo OFF and Alarms
Set the parameters to specify the motor stopping methods to use when the servo is turned
OFF and when an alarm occurs. Refer to the following sections for details on settings.
5.2.1 Stopping Method for Servo OFF
5.2.2 Servomotor Stopping Method for Alarms
There are the following four stopping methods.
There are the following three conditions after stopping.
Motor Stopping Method
Meaning
Stopping by Applying the
Dynamic Brake
The electric circuits are internally connected to stop the Servomotor quickly.
Coasting to a Stop
The motor stops naturally due to friction during operation.
Zero-Speed Stop
The speed reference is set to 0 to stop the Servomotor quickly.
Decelerating to a Stop
Emergency stop torque is used to decelerate the motor to a stop.
Status after Stopping
Meaning
Dynamic Brake Applied
The electric circuits are internally connected to hold the Servomotor.
Coasting
The SERVOPACK does not control the Servomotor. (The machine will move in
response to a force from the load.)
Zero Clamping
A position loop is created and the Servomotor remains stopped at a position
reference of 0. (The current stop position is held.)
•
The dynamic brake is used for emergency stops. The dynamic brake circuit will operate fre-
quently if the power supply is turned ON and OFF or the servo is turned ON and OFF to start
and stop the Servomotor while a reference input is applied. This may result in deterioration of
the elements inside the SERVOPACK. Use speed input references or position references to
start and stop the Servomotor.
•
To minimize the coasting distance of the Servomotor to come to a stop when an alarm occurs,
zero-speed stopping is the default method for alarms to which it is applicable. However,
depending on the application, stopping with the dynamic brake may be more suitable than
using a zero-speed stop.
For example, when coupling two shafts (twin-drive operation), machine damage may occur if a
zero-speed stopping alarm occurs for one of the coupled shafts and the other shaft stops with
a dynamic brake. In such cases, change the stopping method to the dynamic brake.
•
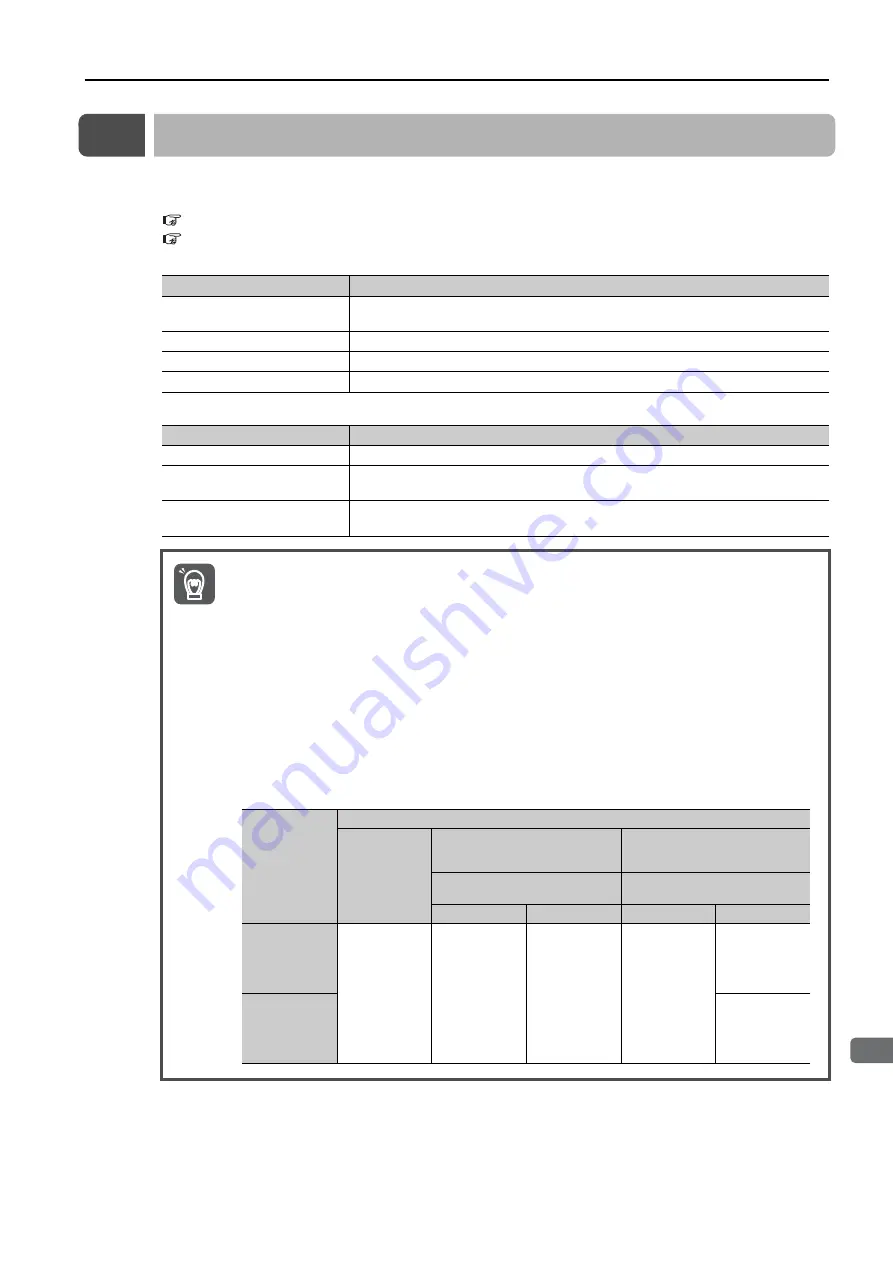
If you turn OFF the main circuit power supply or control power supply during operation before
you turn OFF the servo for a SERVOPACK that supports the dynamic brake hardware option
specifications, the Servomotor stopping method depends on the SERVOPACK model as
shown in the following table.
Important
Condition
Servomotor Stopping Method
SGD7S-R70A,
-R90A, -1R6A,
-2R8A, -R70F,
-R90F, -2R1F,
and -2R8F, and
SGD7W-1R6A
and -2R8A
SGD7S-3R8A, -5R5A, -7R6A,
-120A, -180A, and -200A,
and SGD7W-5R5A and -7R6A
SGD7S-330A, -470A, -550A,
-590A, and -780A
External Dynamic Brake
Resistor
External Dynamic Brake
Resistor
Not connected
Connected
Not connected
Connected
Main circuit
power supply
turned OFF
before turning
OFF the servo
Coasts to a
stop.
Coasts to a
stop.
Stops with the
dynamic brake.
Coasts to a
stop.
Stops with the
dynamic brake.
Control power
supply turned
OFF before
turning OFF
the servo
Coasts to a
stop.






























