Operation Manual 37107F
MFR 3 - Multi Function Relay
Page 34/165
© Woodward
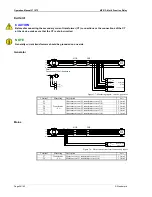
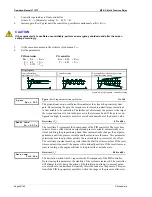
Direction of Power
≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡
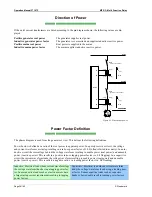
If the unit's current transformers are wired according to the pin diagram shown, the following values are dis-
played:
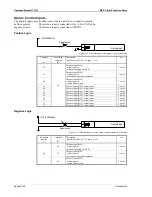
Positive generator real power
The generator supplies real power.
Inductive generator power factor
The generator is overexcited and supplies inductive reactive power.
Positive mains real power
Real power is supplied to the mains.
Inductive mains power factor
The mains supplies inductive reactive power.
MFR 3
26
25
G
28
27
pos
Q
P
ind
pos
Q
P
ind
GENERATOR
generator circuit breaker
GCB
mains circuit breaker
MCB
MAINS
BUSBAR
GENERATOR
s2 (l)
S2 (L)
s1 (k)
S1 (K)
s2 (l)
S2 (L)
S1 (K)
s1 (k)
Figure 4-1: Direction of power
Power Factor Definition
≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡≡
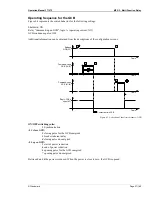
The phasor diagram is used from the generator's view. This defines the following definitions.
Power Factor is defined as a ratio of the real power to apparent power. In a purely resistive circuit, the voltage
and current waveforms are instep resulting in a ratio or power factor of 1.00 (often referred to as unity). In an in-
ductive circuit the current lags behind the voltage waveform resulting in usable power (real power) and unusable
power (reactive power). This results in a positive ratio or lagging power factor (i.e. 0.85lagging). In a capacitive
circuit the current waveform leads the voltage waveform resulting in usable power (real power) and unusable
power (reactive power). This results in a negative ratio or a leading power factor (i.e. 0.85leading).
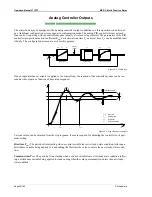
Inductive: Electrical load whose current waveform lags
the voltage waveform thus having a lagging power fac-
tor. Some inductive loads such as electric motors have
a large startup current requirement resulting in lagging
power factors.
Capacitive: Electrical load whose current waveform
leads the voltage waveform thus having a leading pow-
er factor. Some capacitive loads such as capacitor
banks or buried cable result in leading power factors.