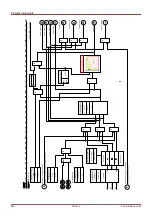
Protective Elements
LVRT – Low Voltage Ride Through [27(t)]
Available Elements:
LVRT[1] ,LVRT[2]
Why LVRT? - Motivation for LVRT
The rapid development of distributed resources (DR) based on the renewable energy such as wind, solar and
others has been changing the electric power system and concepts for its control, protection, metering and
communication rapidly, too.
One of the important challenges for the interconnection between the DR and local electric power system (EPS) is
the behaviour of the DR during disturbances within the electrical power system. Most of the disturbances within the
EPS are characterized mainly by non-permanent system voltage collapses (voltage dip/sag) with different time
durations.
According to traditional protection concepts a distributed energy resource should be tripped as fast as possible from
the grid in case of a significant low voltage condition. This is no longer acceptable because of the continuous rising
share of distributed energy resources within the energy market. Uncontrolled disconnecting significant parts of the
power generation during disturbances within the grid endangers the system stability of the electrical power system.
It was reported
3
that during system fault with low voltage drops, a complete 5000 MW wind park (without LVRT
capability) was decoupled from the electrical power system. The consequence was a dangerous system voltage
and frequency instability.
Based on experiences like that, lots of electric utilities and state public utilities have issued interconnection
standards which require Low-Voltage-Ride-Through (LVRT) capability during EPS disturbances.
What does LVRT mean in detail?
It is no longer allowed to decouple/disconnect a DR from the grid just because of a non-permanent voltage dip.
Protective relays and control units have to take this into account.
Instead of that, the distributed resource has to be able to ride through such disturbances according to a
LVRT
profile. The shape of this
LVRT profile is very similar according to the different guidelines within different countries
or local utilities. But they could differ in details.
By means of
LVRT the system stability is improved in situations, when the contribution of DRs is needed mostly.
The importance of
LVRT will rise with the growing share of DRs within the electrical power system.
Based on the technical requirements mentioned above, a
LVRT protection function was developed for the
HighPROTEC product line which covers the LVRT profiles (capabilities) defined by all relevant national and local
grid interconnection standards.
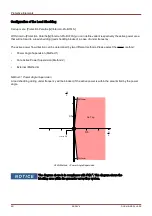
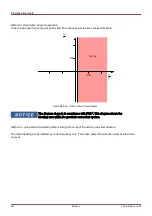
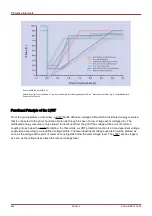
The following drawing shows details on the different
LVRT standards in different countries. Please note, that the
standards and hence the grid codes are in some countries still under development.
961
MCDLV4
DOK-HB-MCDLV4-2E
Содержание HighPROtec MCDLV4
Страница 1: ...Manual Line Differential Protection MCDLV4 Software Version 3 4 a DOK HB MCDLV4 2E Revision A English...
Страница 3: ...Order Code Order Code 3 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E...
Страница 47: ...Installation and Connection 47 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E...
Страница 164: ...Input Output and LED Settings 164 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E...
Страница 433: ...Parameters 433 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E...
Страница 457: ...Device Parameters 457 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E...
Страница 473: ...Blockings 473 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E...
Страница 822: ...Protective Elements Name Description Profibus Scada Cmd 16 Scada Command 822 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E...
Страница 988: ...Protective Elements 988 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E P P Q P Q P Q Q Q P S S...
Страница 989: ...Protective Elements 989 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E Pr Q P Q P Qr...
Страница 1023: ...Protective Elements 1023 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E...
Страница 1070: ...Supervision 1070 MCDLV4 DOK HB MCDLV4 2E...