95x Series Operating Manual - May 17, 2022
Page
44
of
155
The breakdown limit is always enforced throughout the step. Leakage limits are only enforced during the dwell
period of the step. When performing DC Voltage Withstand Testing this allows the user to set different limits
during the ramp (i.e., charging) and dwell periods of the step by using the breakdown and maximum leakage limits
respectively.
A minimum leakage limit can be disabled by setting it to zero (or an unlimited resistance).
A summary of the guidelines for setting breakdown and leakage limits is
–
•
If Pulse Voltage Withstand Testing
–
set a breakdown limit (no leakage limits are available).
•
If the user has both breakdown and maximum leakage limit requirements
–
set them both according to
the requirements. ACez or DCez types cannot be used.
•
If the user has no breakdown limit requirement, only a leakage limit
–
set the maximum leakage limit
according to the requirement and set the breakdown limit significantly higher than this (but low enough
to protect the DUT should it breakdown).
•
If the user wishes to detect breakdown by using the averaged leakage measurement
–
set the maximum
leakage limit according to the requirement (use the RMS equivalent for the AC types) and set the
breakdown limit significantly higher than this (but low enough to protect the DUT, should it breakdown).
ACez or DCez types cannot be used.
•
Otherwise
–
o
For the ACez or DCez types
–
set the maximum leakage current limit according to the breakdown
limit requirement (use the RMS equivalent for the ACez type).
o
For all other types - set the breakdown limit according to the requirement and either disable the
leakage limits entirely (only for the ACW type) or set the maximum leakage limit equal to or
higher than the breakdown limit.
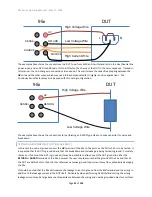
BREAKDOWN CURRENT
A breakdown of a DUT is a sudden, generally heavy, flow of current which does not cease without a reduction in
the applied voltage. Many standards bodies (including UL) define breakdown as the sudden uncontrolled flow of
current, this is effectively the same definition but is more ambiguous.
Often the user is testing products for compliance with safety standards which specif
y that the DUT “shall not
breakdown” but do not specify a particular current level at which to detect breakdown. It is the industry norm to
set a limit at some level above the normal leakage current level drawn by the DUT. Typically, this is a limit of
10mApk (or 7mArms), but this may need to be increased if the DUT has significant leakage or reduced if the DUT
has little leakage.
There are four breakdown detectors in the 95x which are active throughout all types of Voltage Withstand tests;
these are listed below in order of decreasing speed (the 3
rd
listed is set by the user breakdown limit, the others are
fixed) -
•
The 95x AC and DC voltage supplies have a protective trip mechanism which shuts down the voltage if a
large peak current flows beyond its capability to supply surge current (for this limit see Surge Current
Limiting and Shutdown in the relevant Specifications section for the test type being run). Typically, this
detected and shuts down the test within 30usec (this is indicated as BREAKDOWN).
•
If a step is not set for DUT GROUNDED (option HSS only) and is set for a breakdown limit less than 7mApk,
then the 95x continuously monitors the peak current in the
HV
terminal and shuts down the voltage if this