14
Värmebaronen EP 26E and EP 42E
Installation must take place according to existing
rules and standards. Heating systems can differ from
one country to the next due to climate, traditions and
national regulations. In cases where standards violate
national regulations, the latter must be followed. National
and individual requirements must be taken into account.
The boiler is mounted horizontally so that air which is
released can get out.
The boiler is placed indoors in a suitable location. It can
be placed directly on floor level.
The boiler must be installed vertically with at least
1 metre free space in front of the boiler.
The ambient temperature must not exceed 30°C.
An electric boiler fitted with a closed expansion tank must
undergo an installation inspection prior to first operation.
The inspection must be carried out by a person who is
qualified for the task. The boiler or expansion tank may
not be replaced without another inspection.
Valves must be fitted between the boiler and the heating
system.
Cables and pipes must be laid so that it is possible to
open the front and remove the roof plate for service.
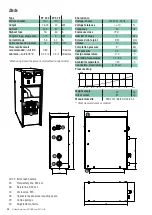
For minimum ceiling height, see Technical data.
The boiler is designed so that it is not damaged if forced
circulation ceases. The system does not need to be fitted
with double circulation pumps or flow guards.
Do not drill into the boiler's cover plates.
Cuttings can damage the boiler's electrical
equipment!
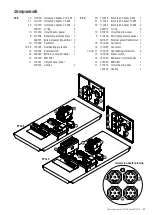
M6 bolts are available for fixing cable trays.
Water quality
Tap water is usually classified from the point of view of
hygiene. Good water classified on this basis is not automatically
suitable for a heating system. To avoid problems a technical
water analysis should take place. Any nonconformities with
standard values should be corrected.
If the volume of the heating system is low, the boiler and
heating system may be filled with water that is not classified
as good boiler water. When the water is heated, some oxygen
and carbonic acid are emitted to the expansion tank or vent
valves. The remainder will react with the metals in the system.
This corrosion is often insignificant as the same volume of
water circulates and it soon becomes oxygen-free. What is
important is that the system is leak-proof so that the water is
not replaced with new oxygen rich water and the water is not
oxygenated during operation.
In large systems, it is impossible, in practice, to protect
against leaks and oxygen admission. In such cases, an
oxygen-consuming agent can be added so that there is
always a slight surplus in the system. These agents often
contain corrosion-limiting additives.
Suitable water line quality:
Alkalinity
≥
60 mg/l to avoid corrosion.
Carbonic acid content > 25 mg/l increase the risk of corrosion.
Sulphate contents > 100 mg/l may accelerate corrosion.
If the sulphate content is higher than the alkalinity, there is
a risk of copper corrosion.
Hard water causes boiler scale and is not suitable in
a heating system.
Very soft water may cause corrosion damage.
Chloride levels above 100 mg/l make the water aggressive,
especially together with lime deposits.
Low pH values may cause corrosion damage. The pH value
should be between 7.5 and 8.5.
The presence of carbonic acid in combination with low pH
and hardness values makes the water aggressive.
Flow direction
The circulation pump must press the water through the boiler
with the flow direction shown in the figure.
Frost protection
If the water is mixed with ethylene glycol, it is important
to check that it contains a suitable quantity of corrosion-
protection additive. When ethylene glycol breaks down,
one of the by-products is carbonic acid, which increases
the risk of corrosion.
Flow requirements
The boiler must have a constant, adequate flow to function
satisfactorily.
Insufficient water flow can result in the following problem:
• The difference between the temperature setting and the
actual temperature achieved in the boiler increases.
• Irregular control with increased wear on the boiler's relays
and contactors, with reduced service life as a result.
Excessive water flow may result in the following problems:
• Vibrations in the immersion heaters with noise and reduced
service life as a result.
• Unnecessary wear on the system's components.
The boilers can withstand zero flow from a safety point
of view, but in order to get a good adjustment and
avoid unnecessary wear on the components, the flow
recommendations should be followed.
The higher the operating temperature and temperature
accuracy, the higher the flow rate selected should be.
Pipe installation