NINA-W1 series - System integration manual
UBX-17005730 - R15
System description
Page 13 of 54
C1 - Public
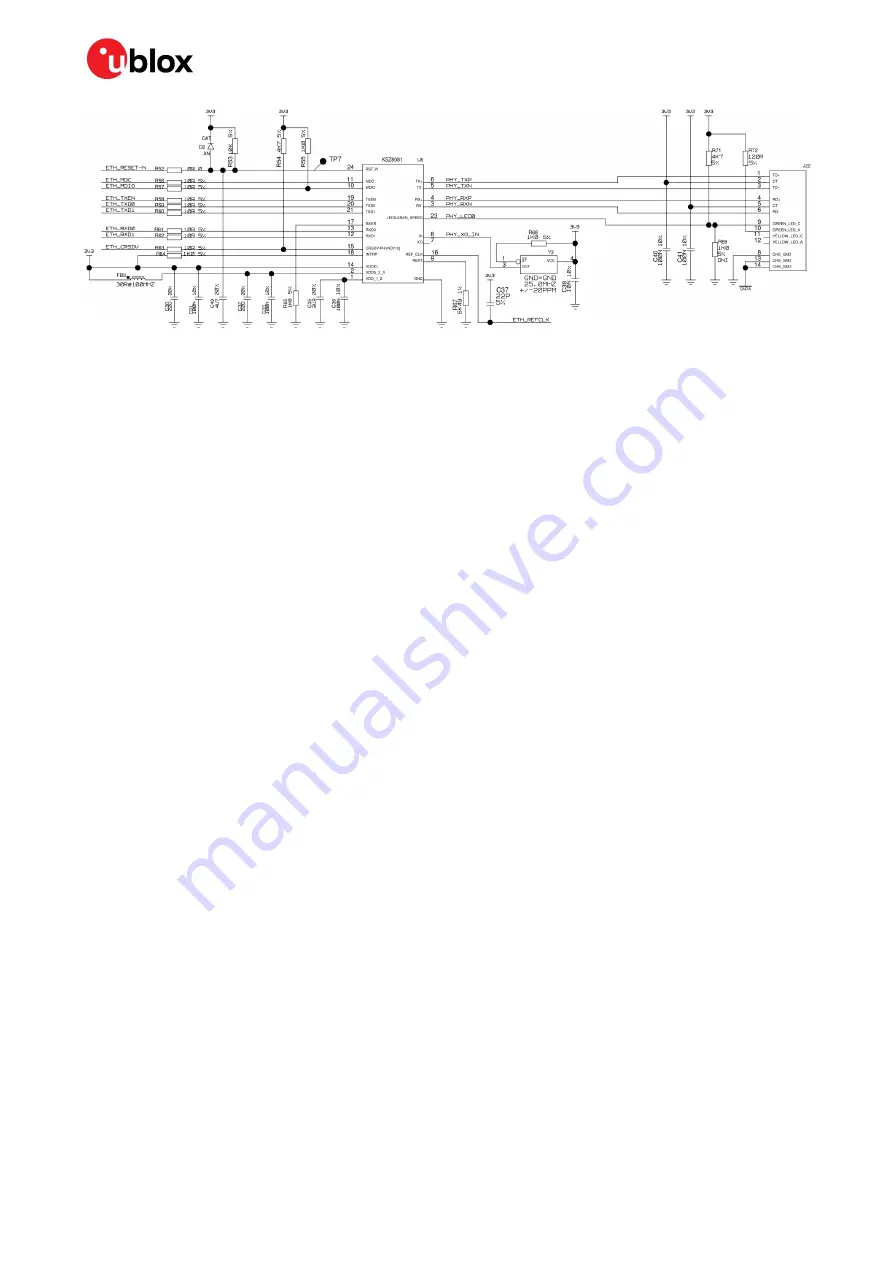
Figure 5: EVK-NINA-W1 Ethernet PHY implementation
1.7.2.3
MAC to MAC connection
When connecting NINA-W1 series modules using a direct MAC to MAC connection, the SMI interface
can be left unconnected. Depending on the routing of the RMII interface on the host PCB, termination
resistors can also be needed.
An external 50 MHz oscillator is needed while running a MAC-to-MAC connection.
1.7.3
Serial peripheral interface (SPI)
⚠
NINA-W13 and NINA-W15 modules support SPI from software version 3.0.0 onwards.
In addition to UART support, NINA-W13 and NINA-W15 modules also include a Serial Peripheral
Interface (SPI) for data communication. The module acts as an SPI slave.
The following SPI signals are available:
•
Chip select as input (
SPI_CS
)
•
Data lines (
SPI_MOSI
as input,
SPI_MISO
as output)
•
Clock (
SPI_SCLK
as input)
•
Optional hardware flow control lines (
SPI_NORX
and
SPI_DRDY
as output)
For details on SPI operation, see also the u-connectXpress SPI peripheral protocol specification [10].
1.8
Antenna interfaces
Antenna interfaces are different for each module variant in the NINA-W1 series.
1.8.1
Antenna pin – NINA-W1x1
NINA-W1x1 modules are equipped with an RF pin. The pin has a nominal characteristic impedance of
50
Ω
and must be connected to the antenna through a 50
Ω
transmission line. This allows reception
of radio frequency (RF) signals in the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
Choose an antenna with optimal radiating characteristics for the best electrical performance and
overall module functionality. An internal antenna, integrated on the application board or an external
antenna connected to the application board through a proper 50
Ω
connector, can be used.
When using an external antenna, the PCB-to-RF-cable transition must be implemented using either
a suitable 50
Ω
connector, or an RF-signal solder pad (including GND) that is optimized for 50
Ω
characteristic impedance.