MAX-M5Q - Hardware Integration Manual
FTX-HW-13008
Objective Specification
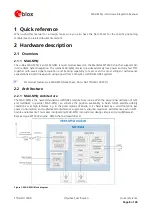
Hardware description
Page 9 of 40
2.3
Power management operating modes
u-blox MAX-M5Q technology offers a power-optimized architecture with built-in autonomous power saving
functions to minimize power consumption at any given time. The receiver operates in two modes: Continuous
mode for best performance or Power Save mode for optimized power consumption. In addition, an integrated
high efficiency DC/DC converter allows low power consumption even for higher main supply voltages.
MAX-M5Q modules have the following operating modes:
•
Continuous mode for best GPS/GNSS performance
•
Power Save modes to optimize power consumption
o
Standby mode
o
Periodic mode
o
AlwaysLocateTM mode
•
Backup state
2.3.1
Continuous mode
Continuous mode uses the acquisition engine at full performance resulting in the shortest possible TTFF and the
highest sensitivity. It searches for all possible satellites until the almanac is completely downloaded. The receiver
switches to the tracking engine to lower the power consumption when:
•
A valid GPS/GNSS position is obtained
•
The entire almanac has been downloaded
•
The ephemeris for each satellite in view is valid
2.3.2
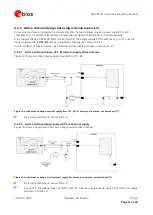
Power Save modes
For power sensitive applications, the MAX-M5Q module also supports low-power operating modes for reduced
power consumption by using the embedded power switch. For more information about the power management
command, see [2]. Use caution when implementing Backup, Periodic or to AlwaysLocate™ mode since forward
compatibility is not guaranteed.
2.3.2.1
Standby mode
In this mode, the receiver stops navigation, the internal processor enters standby state, and the current drain at
main supply
VCC
is typically reduced to 0.4 mA. Enter standby mode by sending the NMEA command:
$PMTK161,0*28. The host can wake up the module from Standby mode to Full Power mode by sending any
byte via the host port.
2.3.2.2
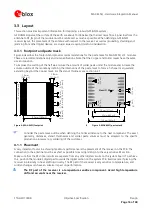
Periodic mode
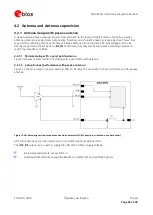
This mode allows autonomous power on/off with reduced fix rate to reduce average power consumption, as
shown in Figure
2 below. The main power supply
VCC
is still active, but turning the supply on and off is
controlled internally by NMEA commands. Enter periodic mode by sending the following NMEA command:
$PMTK225,<Type>,<Run_time>,<Sleep_time>,<2nd_run_time>,<2nd_sleep_time>*<checksum>
where:
•
Type=1 for Periodic Backup mode
•
Run_time = Full Power period (ms)
•
Sleep_time = Standby/Backup period (ms)
•
2nd_run_time = Full Power period (ms) for extended acquisition if GNSS acquisition fails during Run_time
•
2nd_sleep_time = Standby/Backup period (ms) for extended sleep if GNSS acquisition fails during Run_time
Example: $PMTK225,1,3000,12000,18000,72000*16 for periodic mode with 3 s navigation and 12 s sleep in
backup state. The acknowledgement response for the command is $PMTK001,225,3*35. The module can exit
Periodic mode by sending the command $PMTK225,0*2B just after the module wakes up from a previous sleep
cycle.