Tritech International Ltd
Intelligent Gyro Compass
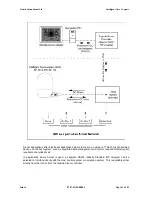
Once the configuration message is correctly received, it is likely that the ‘live’ iGC data will be received
also (particularly if the output data is via the RS232 port on the iGC). For RS485 or Arcnet, there may
be additional work required to commission the interface.
For RS232 output data from the iGC, check the output telegram from the iGC using the terminal
programme. For ASCII protocols this is very easy – just select the correct baud-rate on the terminal
software and power up the iGC. After 5 seconds, the data should appear on the terminal display.
Binary protocols (e.g. Proprietary iGC data or SKR80 data) are more difficult to confirm. There should
however be some data received if the terminal is set at the correct baud-rate – although this data will
not be easily decipherable. Note that SKR80 data only generates printable ASCII characters at certain
heading angles – so rotating the iGC is sometimes required to see data on the terminal screen in this
mode.
8.5
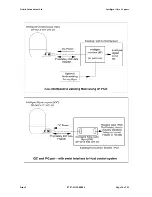
Checking iGC output on an RS485 interface
Checking the data from the iGC when connecting via the RS485 interface may require additional
investigation. One method of checking the output is to use an RS485 to RS232 converter and read the
data with the PC terminal. Alternatively, an oscilloscope may be required to check the state of the
interface lines.
Some common RS485 problems and remedies are noted below:
Data lines A+ and B- crossed – this generates inverted output data that the receiving UART
interprets as multiple ‘Break’ signals. Swap the RS485 wires and check operation –
alternatively use an oscilloscope to check signal voltages;
RS485 bus not correctly terminated – there should be a 120 ohm resistor at each end of the
RS485 bus, but no more than 2 on the bus at any one time. There is a jumper (JP3) o the iGC
PCB that enables this terminator;
Signal ground not connected correctly – The RS485 interface requires that the common-mode
voltage between devices is in the range –7V to +12V typically. The 0V signal ground
connection between the iGC and the Host MUST be connected for reliable performance;
Additional ‘alien’ devices on the RS485 bus – if the iGC RS485 bus is connected other than
‘point-to-point’ from iGC to Host, the other devices on the bus should be approved Tritech
devices, and configured to Tritech specifications. Do not connect non-Tritech devices to the
iGC RS485 bus;
Transmitter enabled on the receiving port – The iGC only enables its transmitter for just
enough time to transmit the complete telegram. At other times the transmitter is disabled and
the iGC is listening for received data. If the Host interface attempts to transmit during the iGC
transmissions data will be lost. If the Host enables its transmitter continually (as is done with
RS422 interfaces), no data will be seen from the iGC;
Receiver not a ‘failsafe’ type and receives ‘Breaks’ when iGC is in Receive mode – this can
occur particularly with older RS485 interface circuits. The receiver does not see an idle (i.e.
nobody transmitting) RS485 pair as idle data – rather it interprets this as inverse polarity (serial
‘Break’ characters). This can be remedied by fitting two resistors to the RS485 signal lines – a
330ohm resistor between A+ and +5V, and a 180 Ohm resistor between B- and ground. This
should be done at the Host end, as the iGC is a ‘failsafe’ receiver device and does not suffer
from this problem.
If the RS485 interface still proves difficult to diagnose, please contact Tritech for assistance.
Issue 2
0707-SOM-00004
Page 24 of 51
Содержание Intelligent Gyro Compass
Страница 13: ...Tritech International Ltd Intelligent Gyro Compass Issue 2 0707 SOM 00004 Page 14 of 51 ...
Страница 30: ...Tritech International Ltd Intelligent Gyro Compass Typical screenshot Issue 2 0707 SOM 00004 Page 31 of 51 ...
Страница 43: ...Tritech International Ltd Intelligent Gyro Compass Appendix F Parts List Issue 2 0707 SOM 00004 Page 44 of 51 ...