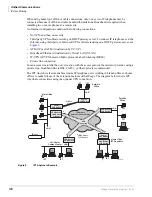
Networking
LAN Deployment
42
IPedge General Description 01/12
the network. IP
edge
can be deployed with a private/static IP address, or it can be deployed with a
public/static IP address as long as it is still behind a firewall.
DHCP Server
– A DHCP server must be installed and configured at each site in order to
automatically provision IP addresses for the IP telephones.
DNS Server
– In an IP system a lot of the underlying communication relies on addressing hosts by
their fully qualified domain names (FQDN). In order for this communication to be successful host
names have to be resolved to IP addresses. For example, SIP trunking configuration uses URIs and
hostnames and these must be resolved to IP addresses using a DNS server. The IP
edge
server
requires that one FQDN be configured, and if IP
edge
meeting is being deployed, a second FQDN
is required.
NTP Server
– It is critical that all networked devices (IP
edge
, gateways and IP phones) are
synchronized to the same clock (system time). The best way to do this is configure all of the
network devices to get and set their respective clocks from a public NTP server.
Firewall/NAT (Network Address Translation) Router
– The IP
edge
server is designed to be
deployed, primarily in a private address space behind a Firewall and NAT router.
•
In order to successfully deploy and manage the IP
edge
system the firewall rules need to be
configured to ensure that all valid incoming traffic is allowed by the firewall. For security
reasons, the firewall should be configured to deny all other traffic.
•
One must configure NAT policies (both inbound and outbound) to map traffic for all IP
edge
services between the WAN public IP address and the LAN IP
edge
private address. The details
on how the NAT policies and Firewall rules need to be configured are described in the
requirements that follow.
•
Recommend network monitoring with a tool such as WhatsUp Gold, OpenNMS, and Zenoss
®
.
Interactions
Network Bandwidth Capacity – On a shared network infrastructure (both data and voice services),
one needs to consider bandwidth requirements for both data and voice.
To provide additional prioritization for voice services, it is possible to enable 802.1p in
conjunction with 802.1q (VLANs). This is currently a system wide setting in IP
edge
. However,
this will enable 802.1p on remote phones requiring the switches are all locations where remote
phones are deployed to support 802.1p.
For IP telephone configuration, broadcast mode is not recommended for large deployments
(greater than 100 phones).
Содержание ID EDGE
Страница 1: ...TOSHIBA Telecommunication Systems Division January 2012 General Description Title Page ...
Страница 6: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Страница 12: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Страница 24: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Страница 128: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Страница 134: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Страница 142: ...This is the last page of the document ...